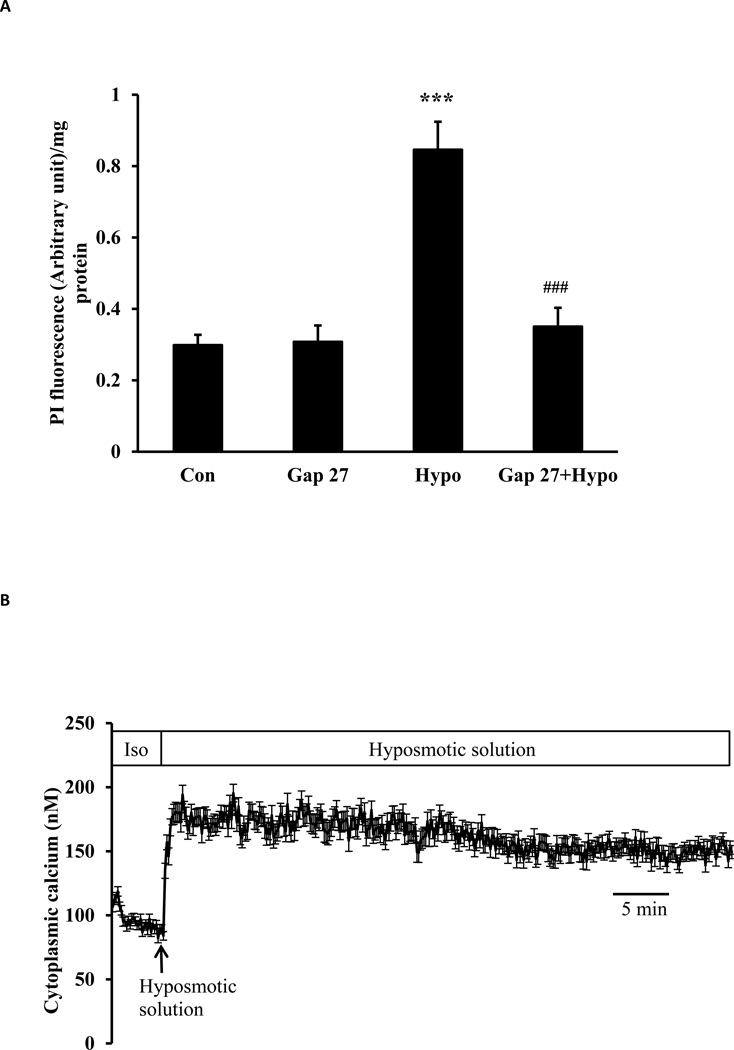
Fig. 1.
Studies on lens epithelial cells exposed to hyposmotic solution (200 mOsm). Panel A shows propidium iodide (PI) uptake. Cells were exposed to 25 µM PI for 30 min in hyposmotic (200 mOsm) solution (Hypo) or control isosmotic solution (Con). Some cells were pre-incubated for 60 min in isosmotic solution containing 200 µM GAP27, a connexin inhibitor, before being exposed to either PI/hyposmotic (GAP 27 + Hypo) or PI/isosmotic solution (GAP 27) in the continued presence of GAP 27. Following the PI uptake period, cells were washed, harvested, homogenized, and PI fluorescence intensity was measured. The results are expressed as relative fluorescence/mg protein. The values are mean ± SE of results from 6 independent experiments. *** indicates a significant difference (p< 0.001) compared to control and ### indicates a significant difference (p< 0.001) compared to hyposmotic treatment alone. Panel B shows the increase in cytoplasmic calcium concentration detected in cells exposed to hyposmotic solution. Using cells loaded with Fura-2, baseline calcium concentration was first measured for 5 min in control isosmotic solution (Iso). Hyposmotic solution (200 mOsm) was then introduced and calcium measurement continued for 1 hour. Data from 15–30 individual cells were averaged and considered as n=1. Results are means ± SE of 5 independent experiments.