Figure 2.
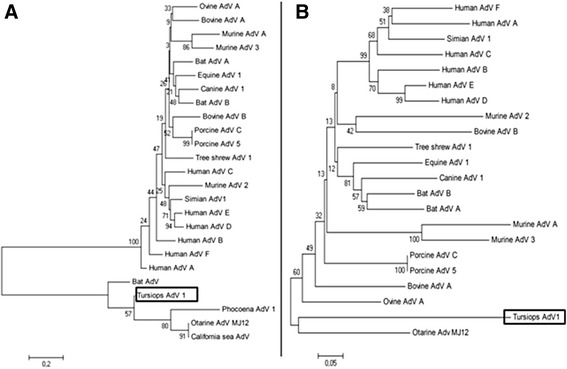
Phylogenetic analysis of adenoviruses based on regions of genes pol and hexon of tursiops adenovirus 1. Neighbor-joining trees were based on amino acid sequences deduced from partial sequences of genes polymerase (pol) (A) and hexon (B) from tursiops adenovirus 1 (enclosed in rectangular frames) and from other selected species of adenovirus (AdV). GenBank accession codes: Bat AdV, AB303301 (for pol); Bat AdV A, GU226970; Bat AdV B, JN252129; Bovine AdV A, NC_006324; Bovine AdV B, AF030154; California sea lion AdV 1, GU979536.1; Canine AdV 1, Y07760; Equine AdV 1, JN418926.1; Human AdV A, NC_001460.1; Human AdV B, NC_001405; Human AdV C, NC_001405; Human AdV D, AC_000006.1; Human adenovirus E, NC_003266.2; Human AdV F, NC_001454.1; Murine AdV A, NC_000942.1; Murine AdV 2, HM049560; Murine AdV 3, EU835513; Otarine AdV MJ12, AB714141 (for pol) and AB714142 (for hexon); Ovine AdV A, NC_002513; Phocoena AdV 1, JN377908.1; Porcine AdV A, NC005869; Porcine AdV 5, AF289262.1; Simian AdV 1, NC_006879; Tree shrew AdV 1, AF258784.1. The MEGA 5.2 software [29] was used to perform for the phylogenetic analysis. P-distance matrices were calculated, and tree topologies were inferred by the neighbor-joining method based on p-distances. Topology reliability was tested by bootstrapping 1000 replicates generated with a random seed. The bars at the bottom indicate relative phylogenetic distance.
