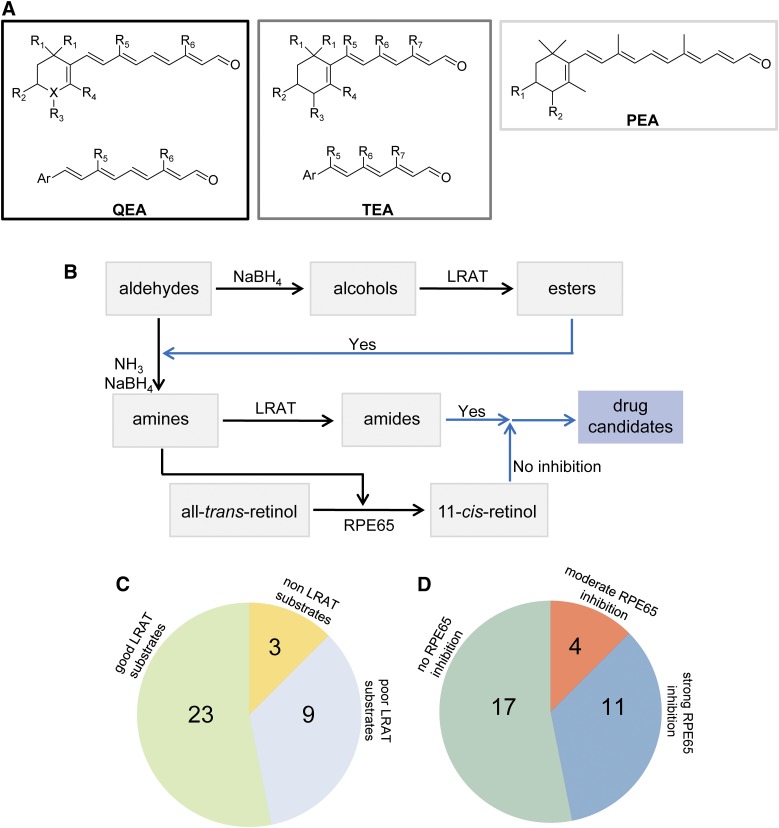
Fig. 2.
Schematic representation of retinoid-based amines and their biologic activities. (A) Retinal analogs. For QEA, R1 and R4 represent H or methyl; R2 and R3 are H, hydroxyl; R5 is H, methyl, t-butyl, benzyl, or p-methoxy benzyl; R6 corresponds to H, methyl, or t-butyl; and X could be C, O, or N. When X is O, there is no R3 group. For QEA-D and QEA-G-001, R5 represents a -(CH2)3- bridge connecting C7 and C9. For TEA, R1 and R4 can be H or methyl, whereas R2 and R3 are H or hydroxyl; R5 is H or t-butyl; R6 can be H, methyl, t-butyl, or benzyl; and R7 corresponds to H or methyl. For PEA, R1 and R2 are H or hydroxyl. These compounds were converted to primary amines prior to the tests. (B) Schematic representation of the experimental design used to test the biologic activity of amines. The black arrows represent the chemical conversions of tested compounds, whereas blue arrows represent the candidate compound selection. (C) Fraction of tested compounds that serve as substrates of LRAT. (D) Extent of inhibition displayed by tested amines against RPE65 enzymatic activity.