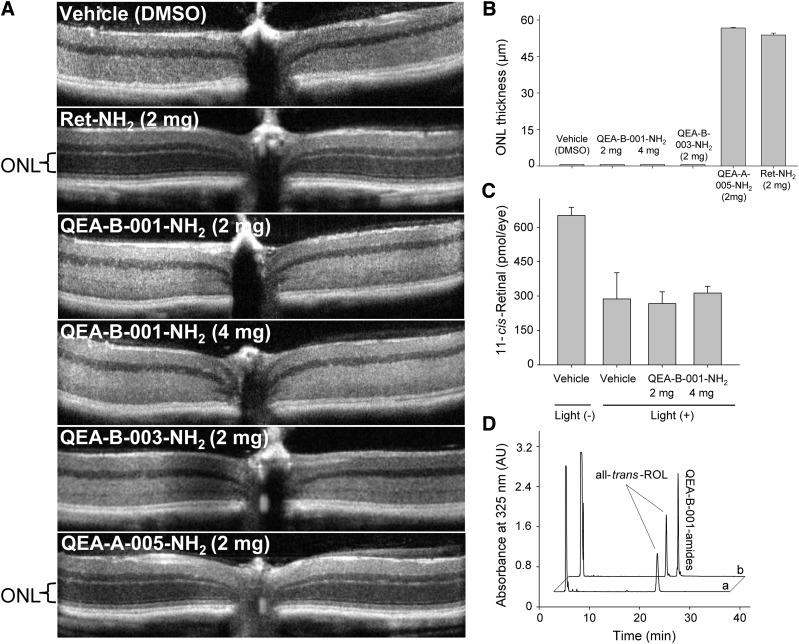
Fig. 4.
Protective effects of selected amines against light-induced retinal degeneration. Four-week-old Abca4−/−Rdh8−/− mice treated with tested amine compounds were kept in the dark for 24 hours and then bleached with 10,000 lux light for 1 hour. (A) Representative OCT images of retinas from mice treated by oral gavage with 2 or 4 mg of different amines. (B) Quantification of the protective effects of QEA-B-001-NH2, QEA-B-003-NH2, QEA-A-005-NH2, and retinylamine (Ret-NH2) is shown by measuring the averaged thickness of the ONL. A dramatic decrease in ONL thickness indicates advanced retinal degeneration. Ret-NH2 (2 mg) and QEA-A-005-NH2 (4 mg) protected the ONLs of these mice. (C) Quantification of 11-cis-retinal in the eyes of mice kept in dark for 7 days after bleaching. The decreased amount of 11-cis-retinal in damaged eyes reflects the loss of photoreceptors. (D) HPLC chromatograph showing acylation of QEA-B-001-NH2 in mouse liver; “a” is a representative chromatogram of a liver extract from mice treated with dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO, vehicle) only, whereas “b” corresponds to an extract from mice treated with 2 mg of QEA-B-001-NH2.