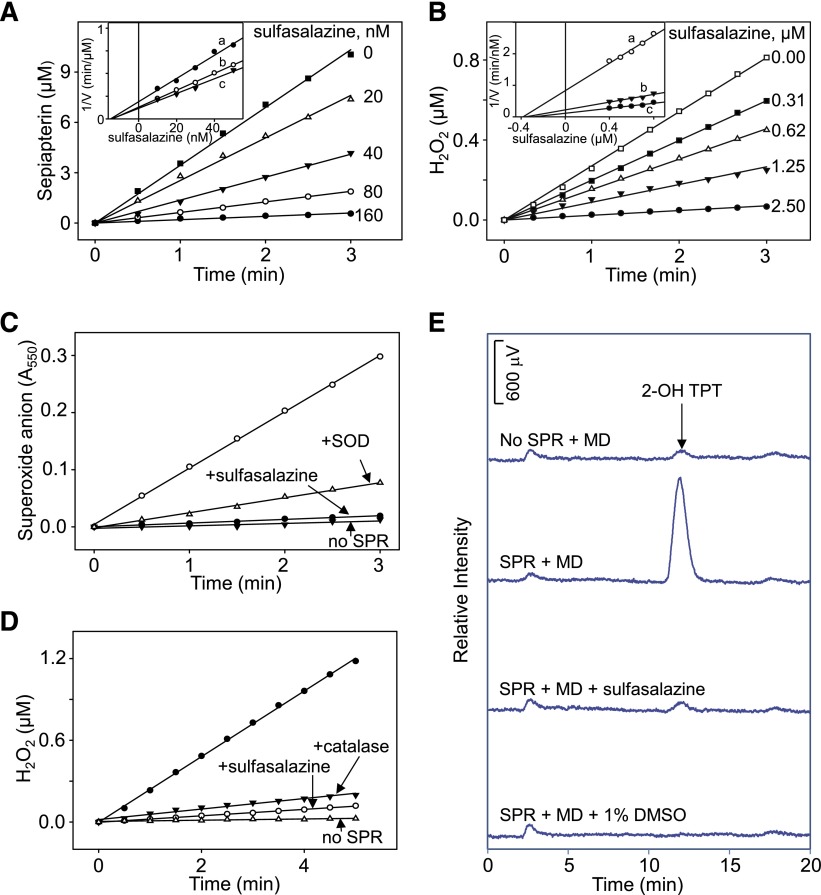
Fig. 2.
Effects of sulfasalazine on human recombinant SPR activity. (A) Inhibition of sepiapterin reduction by sulfasalazine. Sepiapterin reduction was measured by decreases in sepiapterin absorbance at 420 nm. Inset: Dixon plot showing noncompetitive type of inhibition of sepiapterin reduction by sulfasalazine. Reactions were run with increasing concentrations of sulfasalazine in the presence of 25 μM (a), 50 μM (b), or 75 μM (c) sepiapterin. (B) Inhibition of redox cycling of SPR by sulfasalazine. Redox cycling was measured in the presence of 200 μM menadione. In the absence of sulfasalazine, menadione redox cycling induced 23.6 nmol of H2O2/min per milligram of protein. In the absence of menadione, the rate of formation of H2O2 was 0.3 nmol/min per milligram of protein. Inset: Dixon plot showing noncompetitive type of inhibition of redox cycling by sulfasalazine inhibition. Reactions were run with increasing concentrations of sulfasalazine in the presence of 100 μM (a), 200 μM (b), or 300 μM (c) menadione. (C) Effects of 100 μM sulfasalazine on superoxide anion production by SPR. Menadione (MD; 200 μM) was used to induce superoxide anion production; 50 IU/ml superoxide dismutase (SOD) inhibited accumulation of superoxide anion. Superoxide anion was measured spectrophotometrically by monitoring changes in absorbance of acetylated cytochrome c at 550 nm. Reactions were run in the absence and presence of SPR. (D) Effects of 100 μM sulfasalazine on H2O2 production by SPR. Menadione was used to stimulate H2O2 production; catalase (1000 IU/ml) inhibited accumulation of H2O2. H2O2 was measured using the Amplex Red assay. (E) Effects of 100 μM sulfasalazine on the formation of hydroxyl radicals by SPR. Menadione (200 μM) was used to stimulate hydroxyl radical production. Dimethylsulfoxide (1%) was used as a control to trap hydroxyl radicals. Hydroxyl radical production was measured using the terephthalate assay; the product of the reaction, 2-hydroxyterephthalate (2-OH TPT), was used to monitor the formation of hydroxyl radicals. Reactions were run for 10 minutes before analysis.