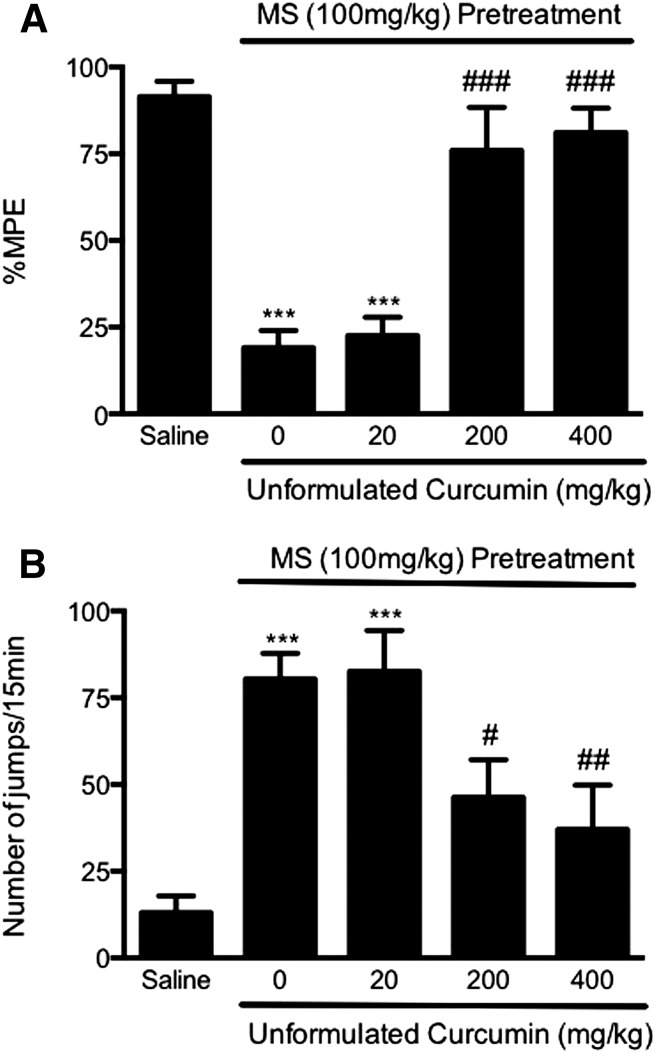
Fig. 1.
Prevention of acute opioid tolerance (A) and dependence (B) by curcumin at high doses. Separated groups of six mice were pretreated with curcumin (20, 200, 400 mg/kg p.o.) or saline before the treatment with morphine sulfate (100 mg/kg s.c.) or saline to induce acute opioid tolerance and dependence. Curcumin (200, 400 mg/kg) significantly attenuated opioid antinociceptive tolerance (A) and physical dependence (B), whereas it was not effective at 20 mg/kg. Data are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. ***P < 0.001 compared with the saline group; #P < 0.05; ##P < 0.01; ###P < 0.001 compared with the morphine (MS) group.