FIG 5.
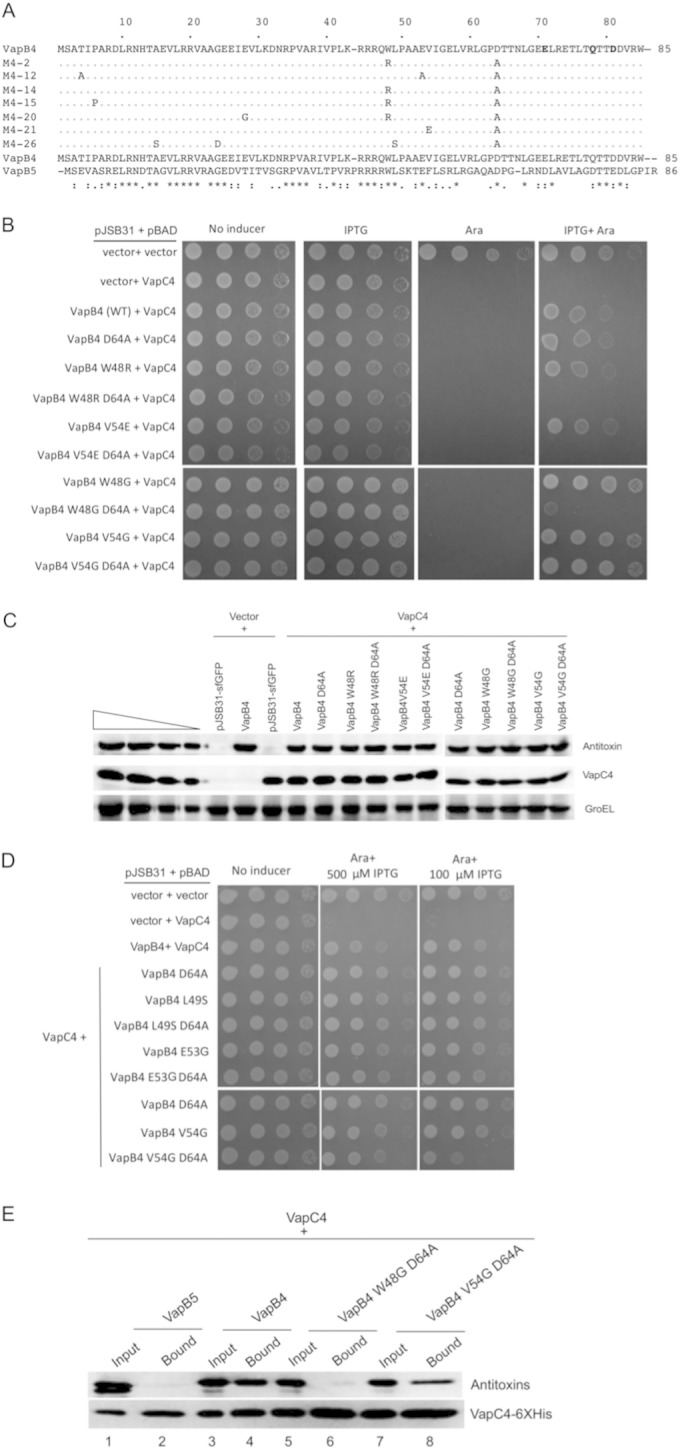
Mutation of W48 results in the loss of antitoxin activity of full-length VapC4 D64A. (A) Comparison of the sequences of VapB4 with those of the defective mutants isolated from screening. (B) Spotting assay for E. coli strain LMG194 carrying the indicated plasmids carried out as described in the legend to Fig. 1B. (C) Western blot analysis was carried out as described in the legend to Fig. 2C. (D) E. coli strain LMG194 carrying the indicated plasmids was grown and spotted with 10-fold dilutions on M9 medium supplemented with 100 μg/ml ampicillin, 30 μg/ml chloramphenicol, and 0.2% glycerol in the presence or absence of 0.02% l-arabinose and 500 μM (or 100 μM) IPTG and grown for 16 h at 37°C. (E) Western blot analysis of copurified proteins from E. coli LMG194 cells carrying plasmids expressing VapB5 or the indicated VapB4 alleles and VapC4-myc-6× His. Cells were induced with 0.02% l-arabinose and 500 μM IPTG for 30 min at 37°C. Western blots were probed with anti-GFP antibody for VapB4 or its mutant proteins and anti-myc antibody for VapC4 proteins.
