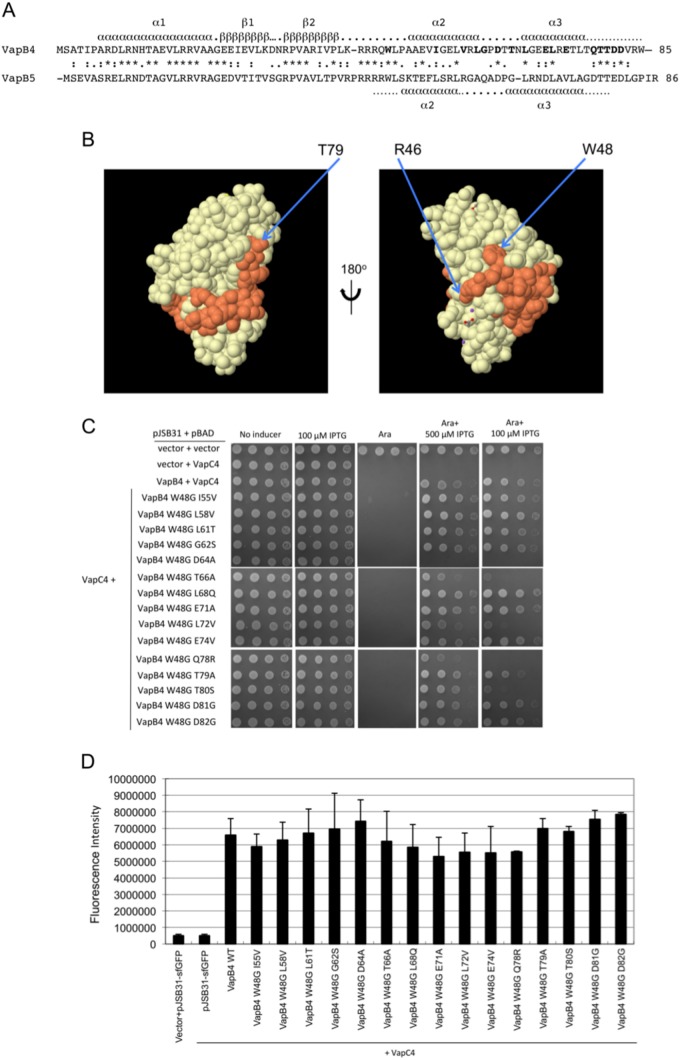
FIG 6.
Mutation of W48 results in the loss of antitoxin activity of full-length VapC4 D64A. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment of VapB4 and VapB5, with their corresponding predicted secondary structure elements assigned. Secondary structure assignments for VapB4 were from the Phyre2 server (43), and those for VapB5 were from reference 37. (B) Structure of the VapB5 (orange)-VapC5 (white) heterodimer (37). The structure with PDB accession number 3DBO was generated by use of the PISA program (44). (C) Spotting assay for E. coli strain LMG194 carrying the indicated plasmids carried out as described in the legend to Fig. 5D. (D) Fluorescence measurements for VapB4 mutants that were assayed for growth and for which the results are presented in panel C. Measurements were taken directly from the third dilution spot on the plate with 100 μM IPTG after determination that all spots in the dilution were in the linear range of detection of the Typhoon 9410 imager. The columns report the average fluorescence intensity from three biological replicates, and error bars illustrate standard deviations. WT, wild type.