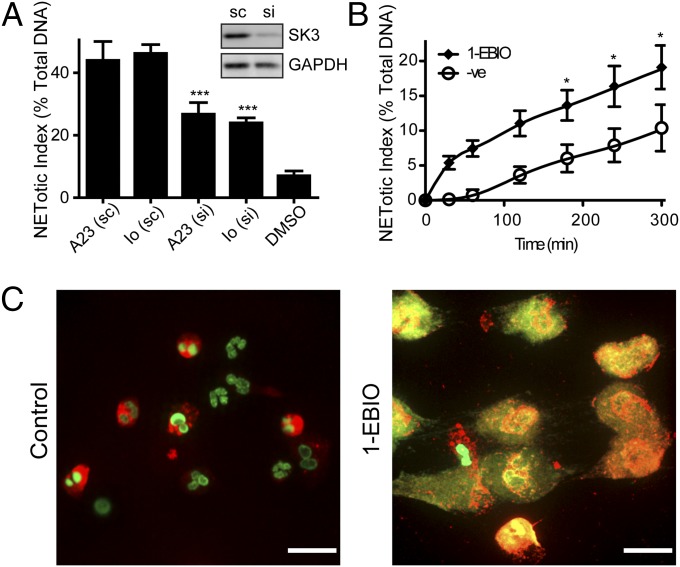
Fig. 6.
SK3 is required for the NOX-independent NETosis. (A) The plate reader assay shows that A23187- or ionomycin-mediated NETosis is significantly reduced in siRNA (si)-transfected dHL-60 cells, compared with scrambled RNA (sc)-transfected control cells at 240 min postactivation (n = 3). Shown above the graph is the result of an immunoblot analysis illustrating a successful knockdown of SK3 protein expression after siRNA transfection (n = 3). Therefore, knockdown of the SK3 channel by siRNA significantly reduces calcium ionophore-induced NETosis. (B and C) SK channel activator 1-EBIO induces NETosis. (B) The plate reader assays were performed to monitor NET release over time in response to the activation with 1-EBIO (n = 5). (C) Immunofluorescence staining confirms that compared with DMSO control, the activation of potassium channels by 1-EBIO induces NET release as shown by the colocalization of DNA (green) and MPO (red) after 300 min. sc, scrambled RNA-transfected cells; si, SK3 siRNA-transfected cells. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 compared with the agonist alone (A, one-way ANOVA; B, two-way ANOVA).