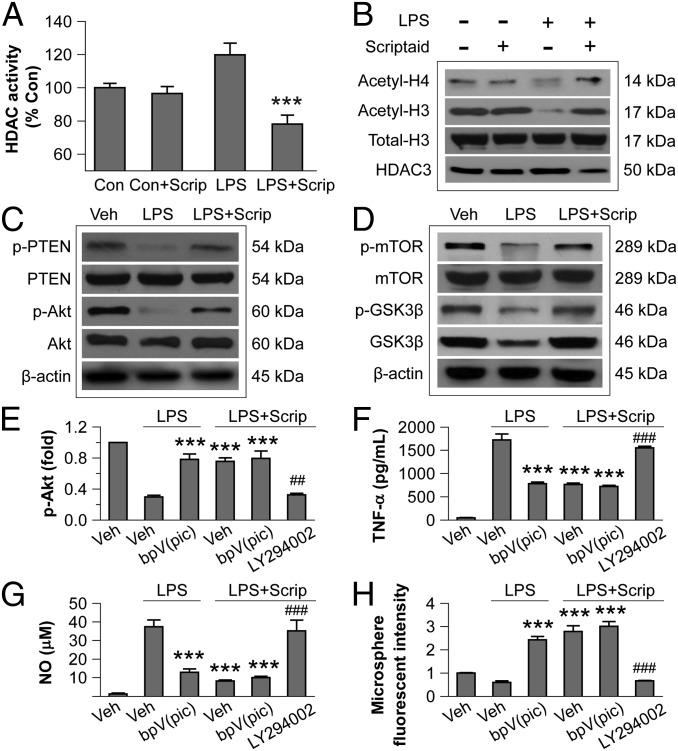
Fig. 5.
HDAC inhibition modulates microglial polarization through the PI3K/Akt pathway. (A) LPS-induced HDAC activity in primary microglia cultures was reduced by Scriptaid. (B) Scriptaid prevented decreases in acetylated-histone 3 (H3) and acetylated H4 in primary microglia at 3 h after LPS, as measured by Western blot analysis. (C) Scriptaid prevented loss of p-PTEN (Ser380/Thr382/383) and p-Akt (Ser473) in LPS-challenged microglia, as measured by Western blot analysis. (D) Scriptaid largely prevented the decrease in p-mTOR (Ser2488) and p-GSK3β (Ser9) levels in LPS-treated microglia. (E) LPS reduced p-Akt levels, an effect largely blocked by the PTEN inhibitor dipotassium bisperoxo (picolinato) oxovanadate [bpV(pic)] (1 μM). Scriptaid partially preserved p-Akt levels in LPS-treated microglia alone or in the presence of bpV(pic), but not in the presence of the PI3K/Akt inhibitor LY294002 (10 µM). (F and G) LPS treatment of microglia increased TNF-α and NO production, an effect reduced by bpV(pic) and by Scriptaid. The effect or Scriptaid was reduced by LY294002, but not by bpV(pic). (H) Microsphere uptake was reduced by LPS alone, but increased by LPS + bpV(pic) or LPS + Scriptaid +/− bpV(pic); the effect of Scriptaid on LPS was blocked by LY294002. Thus, all LPS effects were opposed by Scriptaid, and the effects of Scriptaid were abolished by LY294002 and unchanged by [bpV(pic)]. Data are mean ± SEM values from four independent experiments. ***P ≤ 0.001 vs. LPS alone; ##P ≤ 0.01, ###P ≤ 0.001 vs. LPS + Scriptaid.