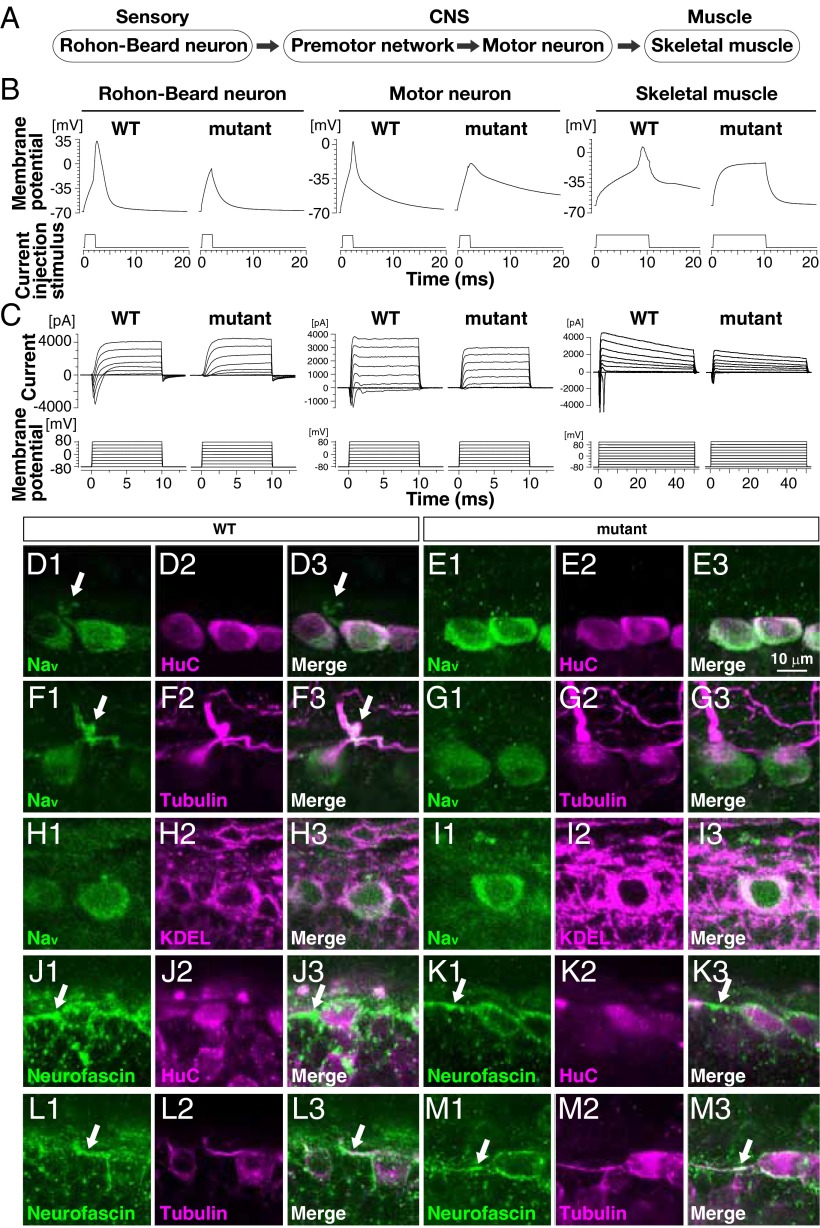
Fig. 2.
NaV channel activity and membrane localization are diminished in mutants. (A) Schematic of the sensorimotor circuit in zebrafish. (B) Whole-cell current-clamp recordings showed that action potentials are elicited in WT RBs, motor neurons, and fast-twitch skeletal muscle. Current injection failed to initiate an action potential in mutant RB cells and most motor neurons and fast-twitch skeletal muscle. (C) Whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings made from indicated cells showing that voltage-dependent inward currents are missing in mutant RBs and motor neurons and significantly diminished in skeletal muscle (Table S3). (D–M) Immunohistochemical labeling of the following proteins in WT and mutant RBs: pan-NaV, the neuronal RNA-binding protein HuC, acetylated α-tubulin common to axons, ER and cis-Golgi proteins containing KDEL tetrapeptides at the C terminus, and neurofascin common to the AIS. Arrows indicate NaV and neurofascin found in the proximal tubulin-positive processes. Note that NaV proteins in the proximal tubulin-positive processes is observed in WT RB cells but not in mutants, whereas neurofascin accumulates at the AIS in WT and mutant RBs.