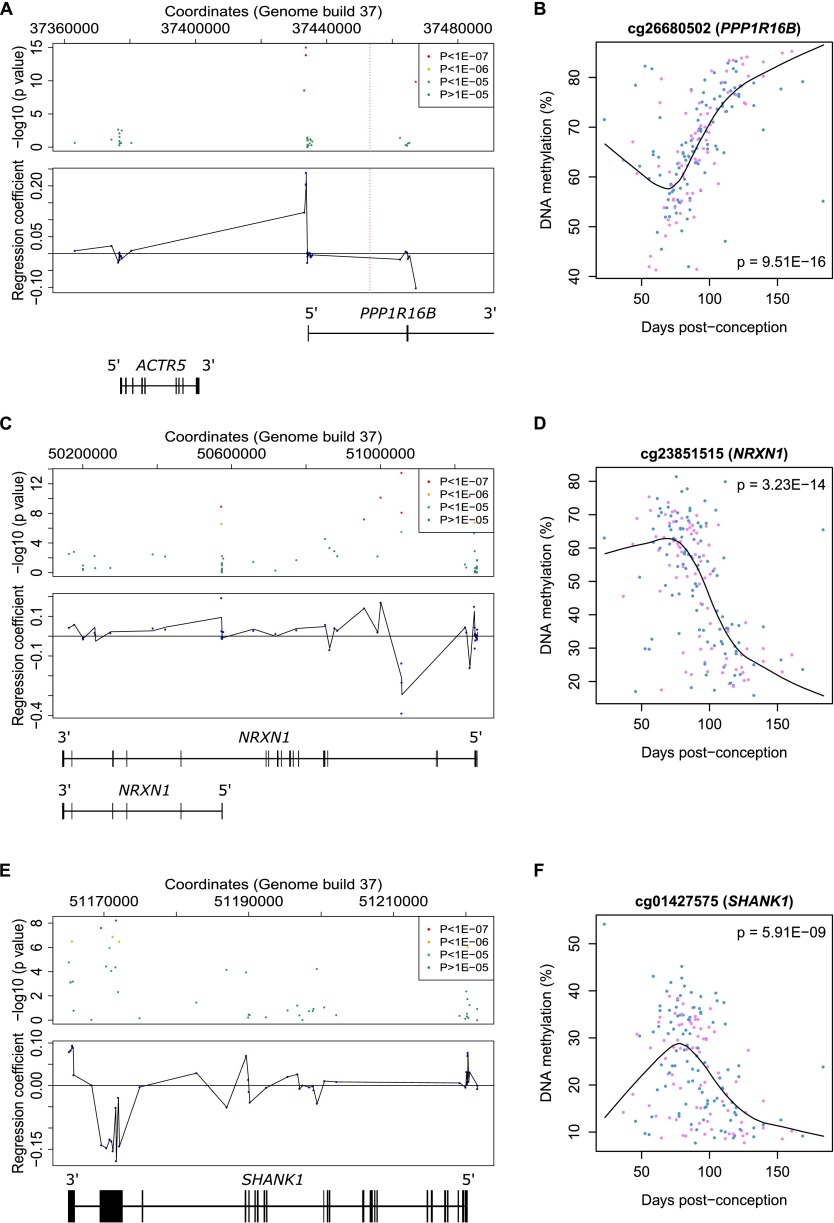
Figure 5.
Fetal brain dDMPs in the vicinity of genetic loci associated with neurodevelopmental disorders. (A) Fetal brain dDMPs within high-confidence regions identified in a recent large GWAS of schizophrenia may provide insight regarding causal variants, e.g., region Chr 20: 37361494–37485994 contains two genes, of which one overlaps with five highly significant dDMPs: PPP1R16B. The position of the most significant SNP (rs6065094) is indicated by a dashed red line. (B) The top-ranked dDMP (cg26680502) in the schizophrenia-associated region displays significant hypermethylation across fetal brain development (P = 9.51 × 10−16). (C) Examples of dDMPs in the vicinity of autism candidate gene NRXN1, with (D) the top-ranked NRXN1 probe (cg23851515) becoming significantly hypomethylated across fetal brain development (P = 3.23 × 10−14). (E) Examples of dDMPs in the vicinity of autism candidate gene SHANK1, with (F) the top-ranked probe (cg01427575) becoming significantly hypomethylated across fetal brain development (P = 5.91 × 10−9).