Figure 2.
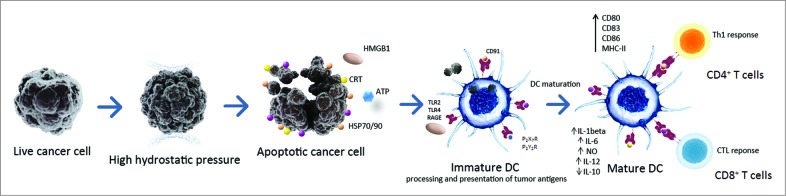
A schematic representation of DC-based vaccine preparation using immunogenic HHP-killed tumor cells. Tumor cells treated with HHP (or other physical ICD-inducing modalities) expose various danger signals, so called DAMPs, in different stages of apoptosis. These DAMPs include calreticulin (CRT), heat shock proteins 70/90 (HSP70/90), HMGB1 and ATP. These molecules bind to respective cognate receptors like CD91 (for CRT/HSPs), TLR2/TLR4 (for HMGB1 or HSP70), P2RX7/P2RY2 (for ATP), respectively, on the cell surface of DCs. This leads to an enhanced engulfment of tumor cells and DC maturation characterized by upregulation of costimulatory molecules such as CD80, CD83, CD86 and HLA-DR, and by a distinct pro-inflammatory cytokine pattern. Activated DCs efficiently present tumor-specific antigens in the context of MHC class I and II molecules to T cells, inducing antitumor CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses. Abbreviations: ATP, Adenosine triphosphate; CRT, calreticulin; CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocytes; DAMPs, danger-associated molecular patterns; DC, dendritic cell; HHP, high hydrostatic pressure; HMGB1, high mobility group box 1 HSP70, heat shock protein 70; HSP90, heat shock protein 90; ICD, immunogenic cell death; P2RX7, P2X purinoceptor 7; P2RY2, P2Y purinoceptor 2; RAGE, receptor for advanced glycation endproducts; TLR, toll like receptor.
