Figure 4.
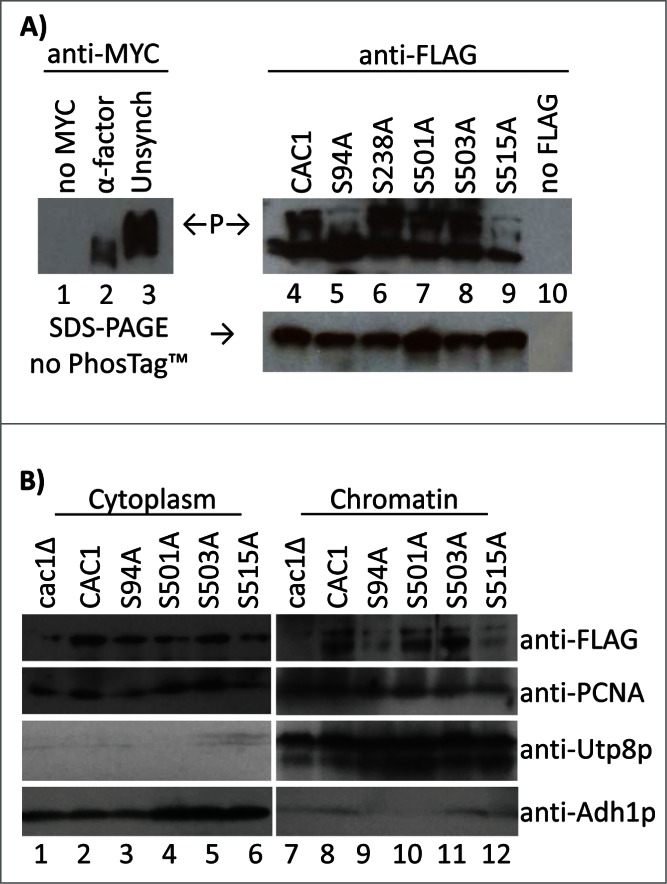
Cac1p-S94A and Cac1p-S515A reduce the association of Cac1p with chromatin. (A) Cells with a MYC-tagged genomic copy of CAC1 (lanes 1–3) or cac1Δ cells with plasmids expressing FLAG-tagged Cac1p with no mutation (CAC1), lane 4, the indicated point mutations (lanes 5–9) or empty plasmid (lane 10) were analyzed by the PhosTagTM retardation assay as inFig. 1. “P” and arrows indicate the mobility of the phosphorylated Cac1p-MYC (left) and Cac1p-FLAG (right). A parallel Western blot without PhosTagTM is shown beneath. One of 2 independent experiments with reproducible outcomes is shown. (B) Spheroplasts from cac1Δ cells with plasmids for the expression of FLAG-tagged Cac1p were lysed and spun to obtain the cytoplasm fractions (lanes 1–6) and chromatin pellets (lanes 7–12). All samples were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-FLAG, anti-PCNA, anti-Utp8p and anti-Adh1p antibodies. Utp8p and Adh1p represent the purity of the chromatin and cytoplasm fractions, respectively. One of 2 independent experiments with reproducible outcomes is shown.
