Figure 2.
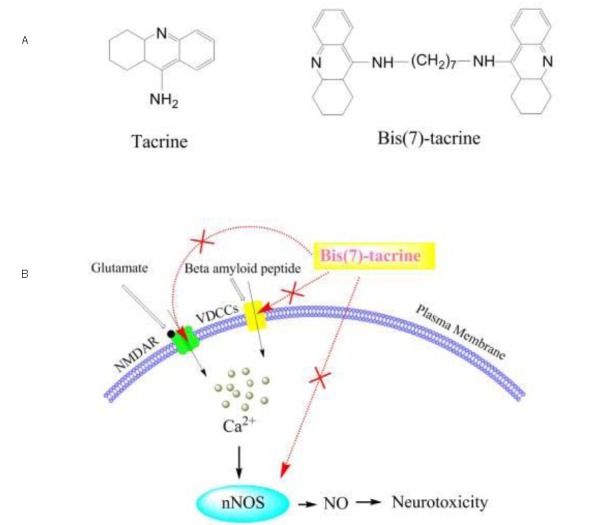
Proposed mechanism of action of bis(7)-tacrine in glaucoma neuroprotection through concurrent blockage of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs), voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels (VDCCs) and neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS).
(A) Chemical structure of tacrine and bis(7)-tacrine.
(B) Synergistic neuroprotection by bis(7)-tacrine via concurrent blockade of NMDAR, VDCCs and nNOS. When retinal ganglion cells are exposed to glutamate and amyloid precursor protein at toxic concentrations, excessive calcium influx mediates the subsequent biochemical events leading to neurotoxicity.
Bis(7)-tacrine concurrently blocks NMDARs, VDCCs and nNOS, thereby synergistically providing substantial neuroprotection. NO: Nitric oxide.
