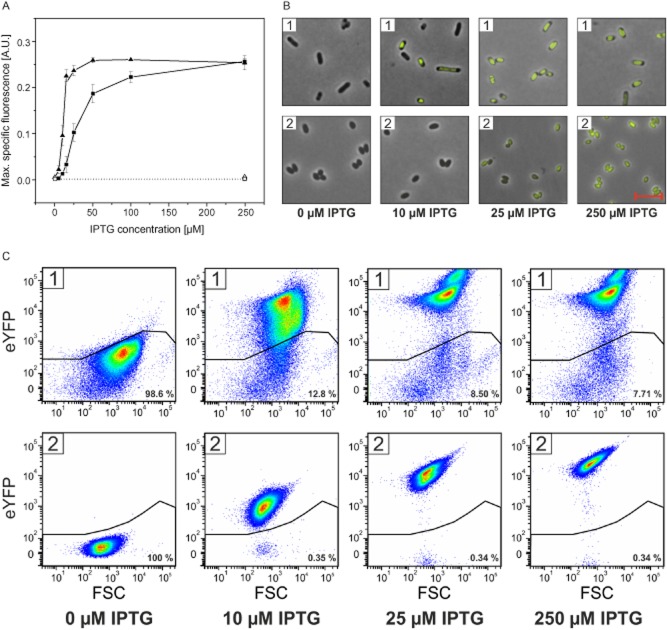
Figure 4.
T7 RNAP-dependent expression of eyfp in C. glutamicum and E. coli. The strains C. glutamicum MB001/pMKEx2-eyfp (□), C. glutamicum MB001(DE3)/pMKEx2-eyfp (▪), E. coli BL21(DE3)/pMKEx2 (Δ) and E. coli BL21(DE3)/pMKEx2-eyfp (▴) were cultivated for 24 h aerobically in 2xTY medium using a BioLector system at 1200 r.p.m. and either 30°C (C. glutamicum) or 37°C (E. coli). Gene expression was induced 2 h after starting the cultivation by addition of 0–250 μM IPTG.A. After 24 h, the maximal specific eYFP fluorescence was determined (ratio of fluorescence emission at 532 nm and backscatter value at 620 nm). Mean values and standard deviations of at least three independent replicates are shown.B. Fluorescence microscopy images of E. coli BL21(DE3)/pMKEx2-eyfp (1) and C. glutamicum MB001(DE3)/pMKEx2-eyfp (2) cultivated with different IPTG concentrations. Images were taken with an exposure time of 40 ms. The red bar represents a length of 5 μm.C. Flow cytometry analysis of E. coli BL21(DE3)/pMKEx2-eyfp (1) and C. glutamicum MB001(DE3)/pMKEx2-eyfp (2) cultivated with different IPTG concentrations. Pseudo-coloured dot plots of eYFP fluorescence versus forward scatter are shown.