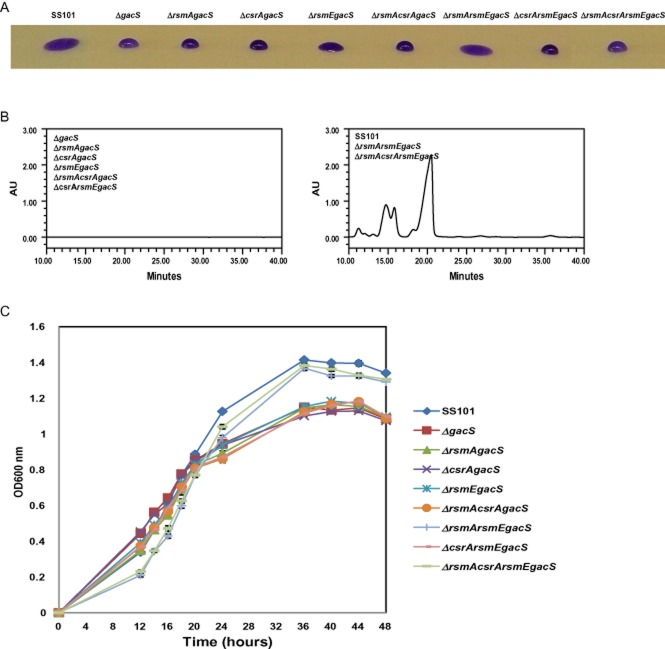
Figure 3.
Phenotypic and chemical analyses of P. fluorescens strain SS101, ΔgacS mutant and single, double or triple mutants disrupted in rsmA, rsmE and csrA in the ΔgacS background.A. Drop collapse assay with cell suspensions of wild-type SS101, ΔgacS, ΔrsmAgacS, ΔcsrAgacS, ΔrsmEgacS, ΔrsmAcsrAgacS, ΔrsmArsmEgacS, ΔcsrArsmEgacS and ΔrsmAcsrArsmEgacS mutants. Bacterial cultures grown for 2 days at 25°C on KB agar plates were suspended in sterile water to a final density of 1 × 1010 cells ml−1, and 10-μl droplets were spotted on parafilm, and crystal violet was added to the droplets to facilitate visual assessment. A flat droplet is a highly reliable proxy for the production of the surface-active lipopeptide massetolide A.B. Reversed phase-high-performance liquid chromatography chromatograms of cell-free culture extracts of wild-type SS101, ΔrsmAgacS, ΔcsrAgacS, ΔrsmEgacS, ΔrsmAcsrAgacS, ΔrsmArsmEgacS, ΔcsrArsmEgacS and ΔrsmAcsrArsmEgacS mutants as described in A. The wild-type strain SS101 produces massetolide A (retention time of approximately 18–21 min) and various other derivatives of massetolide A (minor peaks with retention times ranging from 12 to 18 min) which differ from massetolide A in the amino acid composition of the peptide moiety. AU stands for absorbance unit. Representative chromatograms of ΔrsmAgacS and ΔrsmArsmEgacS mutants are shown.C. Growth of wild-type SS101, ΔrsmAgacS, ΔcsrAgacS, ΔrsmEgacS, ΔrsmAcsrAgacS, ΔrsmArsmEgacS, ΔcsrArsmEgacS and ΔrsmAcsrArsmEgacS mutants in liquid broth at 25°C. At different time points, the optical density of the cell cultures was measured spectrophotometrically (600 nm). Mean values for four biological replicates are given; the error bars represent the standard errors of the mean.