Figure 2.
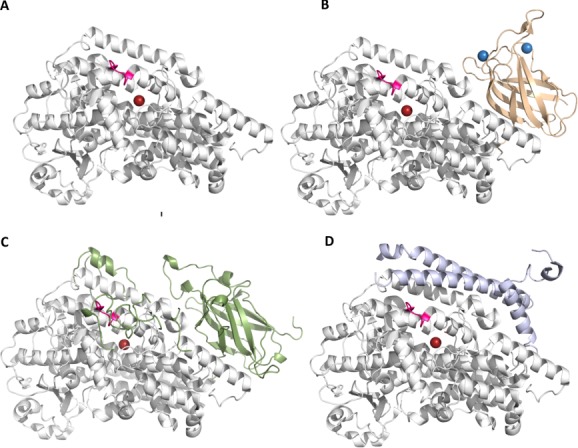
Figure The common core of LOXs is shared by plant, animal and bacterial enzymes. (A) The core domain is a large bundle of helices that houses the catalytic iron. A distinct insertion that contributes to a helix that forms an arch over the active site is colored in bright pink. (B) and (C) The animal (flesh) and plant (green) enzymes have amino terminal domain PLAT domains that may harbor Ca2+ binding sites. (D) The bacterial LOX lacks the PLAT domain, but has additional helices. An interactive view is available in the electronic version of the article.
