Figure 6.
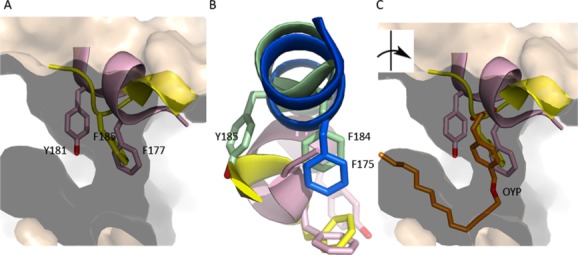
Figure The active site of animal LOXs can be “corked.” (A) The corking amino acids of 5-LOX (pink) and 11R-LOX (yellow) plug what would otherwise be an open U-shaped cavity (15-LOX-2, flesh). (B) The corking amino acids are conserved in “uncorked” LOXs (blue, 12-LOX, green, 15-LOX-2), however since α2 is not “broken” the side chains are distal and cannot seal the active site entrance. The image has been rotated relative to (A) for clarity. (C) In the inhibited structure of 12-LOX an aromatic ring of the inhibitor (gold, OYP) occupies the position of the “cork.”
