Figure 1.
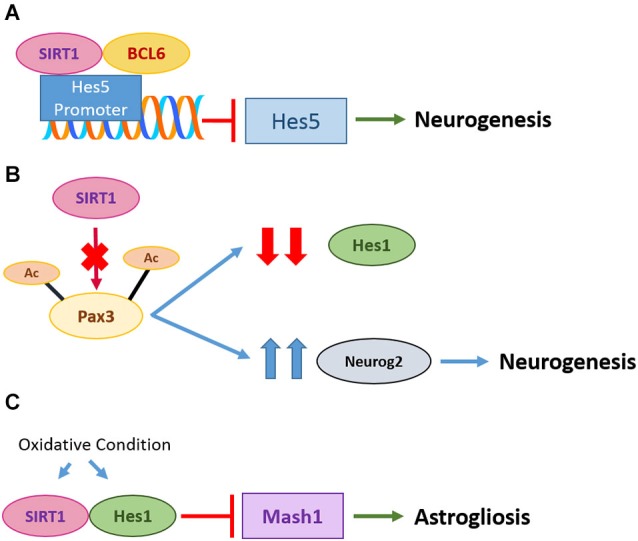
Roles of SIRT1 in neurogenesis and gliogenesis. (A) In neural progenitor cells (NPCs), repression of Notch-dependent Hes5 genes by Bcl6 is important for neurogenesis. Bcl6 triggers exclusion of co-activator Mastermind-like 1 and recruits SIRT1 to inhibit transcription of Hes5, promoting neurogenesis. (B) Pax3 acetylation on C-terminal lysine residues K437 and K475 is critical for regulation of Hes1 and Neurog2. SIRT1 silencing increased acetylation level of Pax3 and subsequently decreased the promoter activity of Hes1 but increased activity of Neurog2, inducing sensory neuron differentiation. (C) Under oxidative condition in NPCs, SIRT1 is upregulated and binds to transcription factor Hes1. This subsequently inhibits pro-neuronal Mash1 and leads to astrogliosis.
