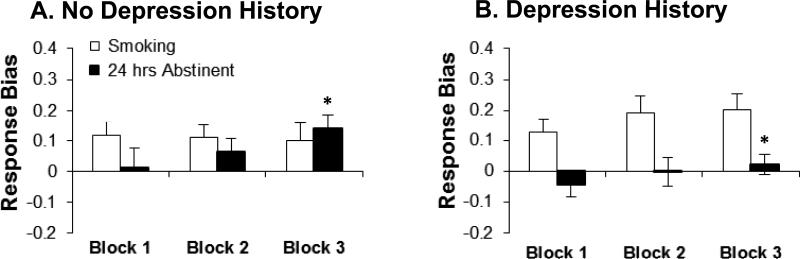
Figure 3. NICOTINE ABSTINENCE AND REWARD RESPONSIVENESS IN HUMANS WITHOUT (N = 14, A) AND WITH (N = 17, B) A HISTORY OF DEPRESSION.
24-hour abstinence from chronic tobacco smoking was associated with decreased response bias in Block 3 for smokers with a history of depression relative to smokers without a history of depression (*p<0.05). Moreover, unlike smokers without a history of depression (A), those with such history failed to develop a response bias towards the more frequently rewarded stimulus (B).