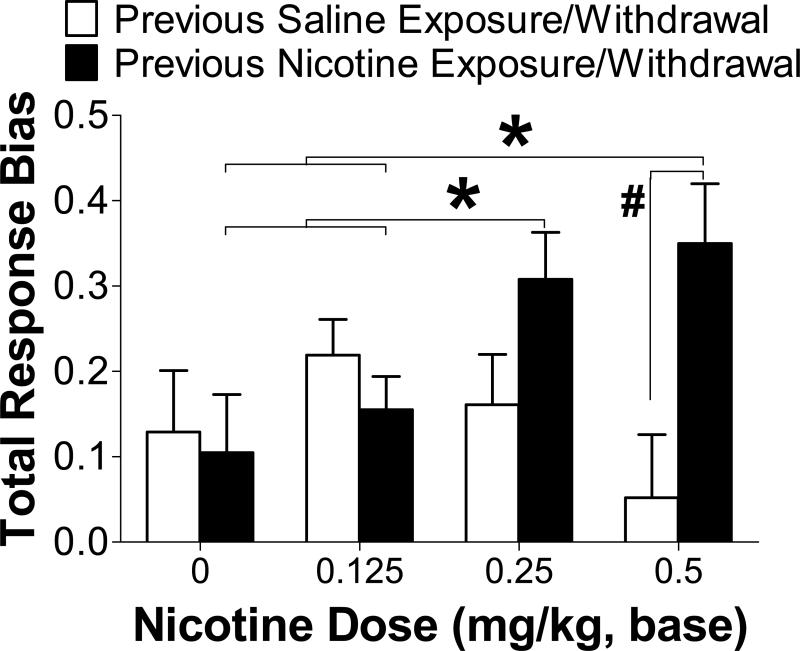
Figure 4. ACUTE NICOTINE-INDUCED CHANGES IN REWARD RESPONSIVENESS IN RATS PREVIOUSLY EXPOSED TO CHRONIC NICOTINE (N = 17) OR SALINE (N = 15).
Acute nicotine re-exposure in rats previously treated with chronic nicotine significantly potentiated response bias compared to acute saline exposure and compared to acute nicotine exposure in rats previously treated with chronic saline. Moreover, acute nicotine treatment did not affect reward responsiveness in previously nicotine-naïve rats. * Different from chronic nicotine-treated rats administered 0 and 0.125 mg/kg acute nicotine (p<0.05); # Different from chronic saline-treated rats administered the same acute nicotine dose (p<0.01).