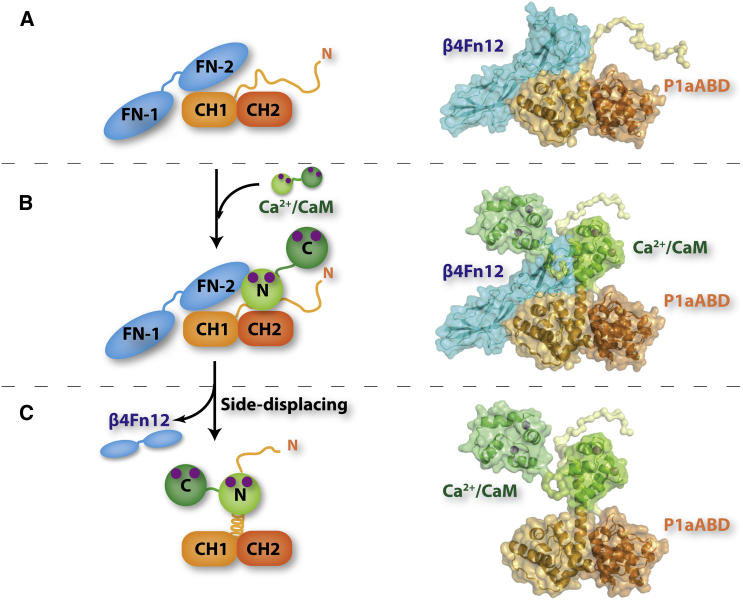
Figure 9.
Model for the CaM-Driven Disruption of the P1aABD/β4Fn12 Complex
(A) At low cytosolic calcium concentrations, the P1a/integrin α6β4 complex is maintained in HDs.
(B) Increased cytosolic calcium concentration, during differentiation or wound healing, leads to activation of CaM (Ca2+-CaM). CaM in its active form binds to the structurally disordered N-ter tail of P1a via its N-ter lobe.
(C) CaM binding leads to the folding of the N-ter tail of P1a into an α helix. The steric clash caused by CaM bound to the α helix results in shunting of integrin β4 from the complex, contributing to HD disassembly.