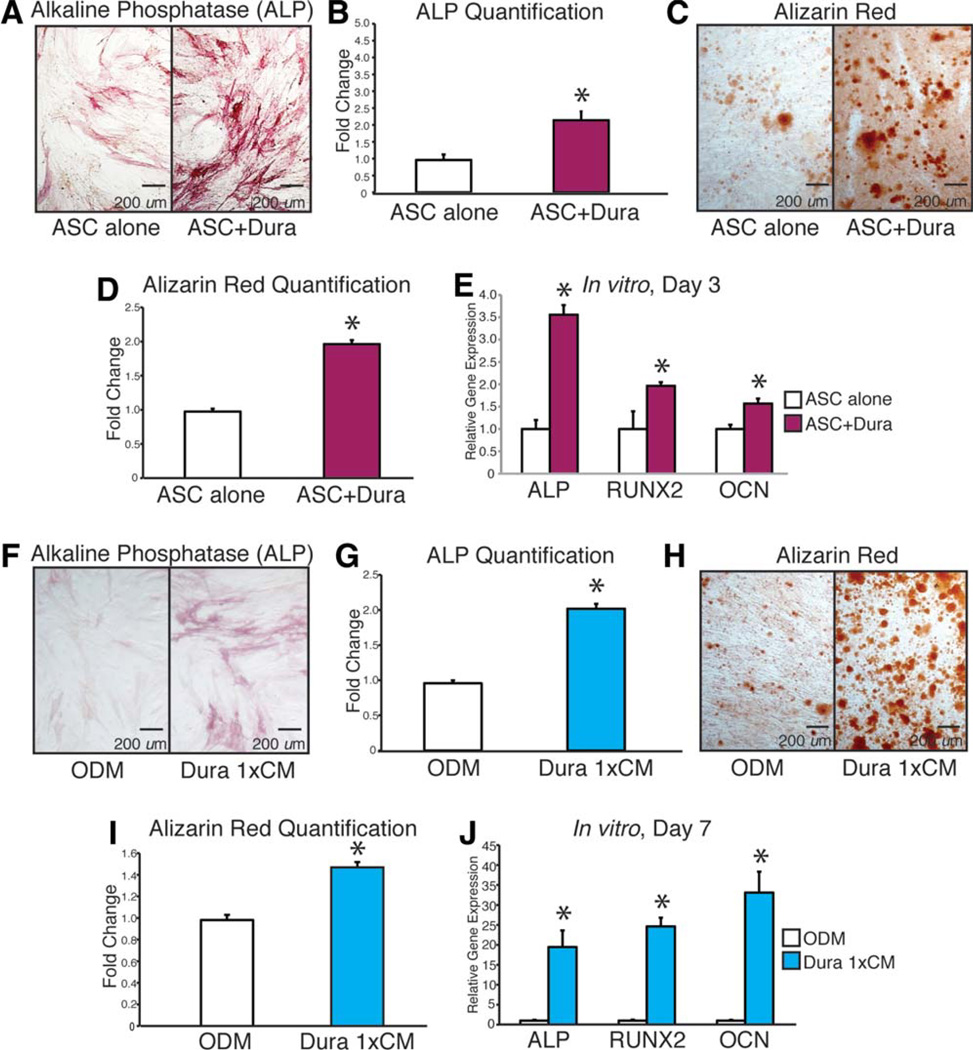
Figure 4.
Mouse dura mater (DM) cells stimulate human adipose-derived stromal cell (hASC) differentiation in vitro. (A–E): hASCs were cultured in osteogenic differentiation medium (ODM) in the presence or absence of mouse DM cells (noncontact coculture). (A, B): Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) stain and quantification of hASCs at 3 days differentiation. (C, D): Alizarin Red stain and quantification of hASCs at 7 days differentiation. (E): Gene expression profile of hASCs at 3 days differentiation grown in the presence or absence of mouse DM cells (noncontact coculture). Markers examined include osteogenic specific genes: ALP, Runt-related protein-2 (RUNX-2), and osteocalcin (OCN). (F–J): Next, hASCs were cultured in ODM with or without the addition of mouse DM cell conditioned media (CM). (F, G): ALP stain and quantification of hASCs at 3 days differentiation. (H, I): Alizarin Red stain and quantification of hASCs at 7 days differentiation. (J): Gene expression profile of hASCs after 7 days differentiation in the presence or absence of DM cell CM. Markers examined include osteogenic specific genes ALP, RUNX-2, and OCN n = 3 for all assays (independent experiments from separately derived cell populations); *, p < .05. A two-tailed Student’s t test was performed to assess significance. Abbreviations: ALP, alkaline phosphatase; ASC, adipose-derived stromal cell; CM, conditioned media; OCN, osteocalcin; ODM, osteogenic differentiation medium; RUNX-2, Runt-related protein-2.