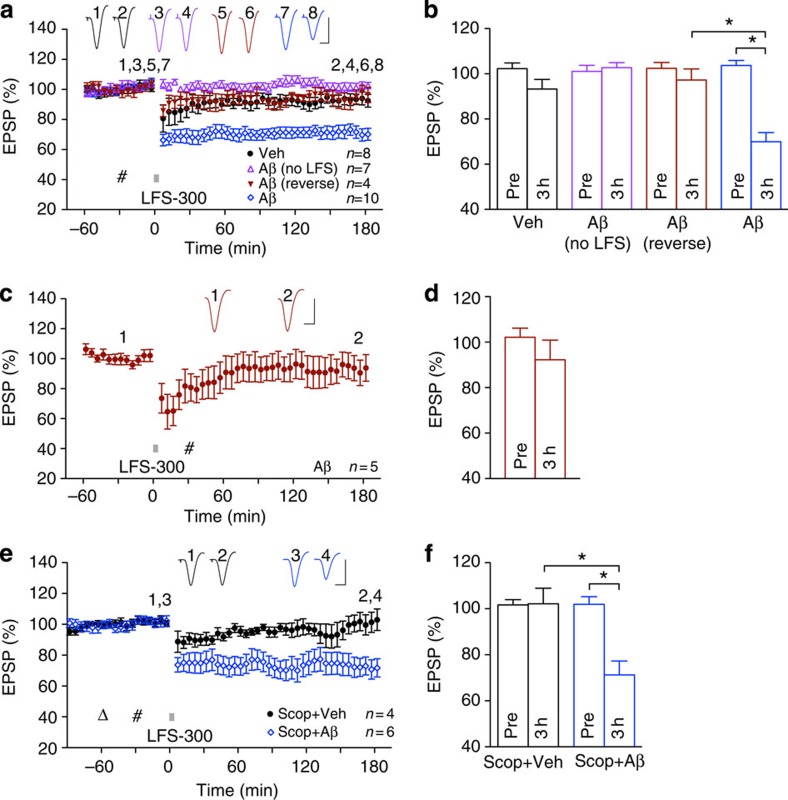
Figure 5. Aβ facilitates the induction of muscarinic receptor-independent LTD by weak low-frequency stimulation.
(a,b) The application of weak LFS (bar, LFS-300; 300 high-intensity pulses at 1 Hz) triggered a robust and stable LTD after acute i.c.v. injection (hash) of 160 pmol Aβ1–42 but not vehicle or the reverse peptide Aβ42–1 (Aβ reverse). This dose of Aβ1–42 did not affect baseline synaptic transmission in the absence of LFS-300 (Aβ no LFS). Data for soluble and protofibril Aβ are combined and some animals had an additional separate i.c.v. injection of 5 μl vehicle 15 min before Aβ. As summarized in (b) at 3 h the EPSP measured 93.3±3.6% in controls (n=8, P>0.05 compared with Pre; paired t), 69.9±3.8% in Aβ-injected rats (n=10, P<0.05 compared with Pre and vehicle group; paired t and one-way ANOVA-Tukey) and 97.3±4.3% in reverse peptide (n=4, P>0.05 compared with Pre). Injection of Aβ1–42 (160 pmol, i.c.v.) did not affect baseline synaptic transmission (102.6±1.6% at 3 h, n=7, P>0.05 compared with Pre). (c,d) Aβ1–42, when administered 15 min after LFS-300 did not facilitate LTD. As summarized in (d) the EPSP was not significantly decreased at 3 h post LFS-300 (92.2 ±8.3%, n=5, P>0.05 compared with Pre; paired t). (e,f) In animals pretreated with scopolamine at the dose (open triangle; 0.2 mg kg−1, i.p.) that completely blocked LFS-induced LTD (see Fig. 2a,b), application of LFS-300 30 min after i.c.v. injection of vehicle did not induce LTD, whereas application of LFS-300 30 min after i.c.v. injection of soluble Aβ1–42 induced a robust and stable LTD. As summarized in (f), at 3 h the EPSP measured 102.2±6.6% in the scopolamine+vehicle group (n=4, P>0.05 compared with Pre; paired t) and 71.2±5.8% in the scopolamine+Aβ group (n=6, P<0.05 compared with Pre or scopolamine+vehicle group; t-tests). Values are mean±s.e.m. Calibration: vertical, 2 mV; horizontal, 10 ms.