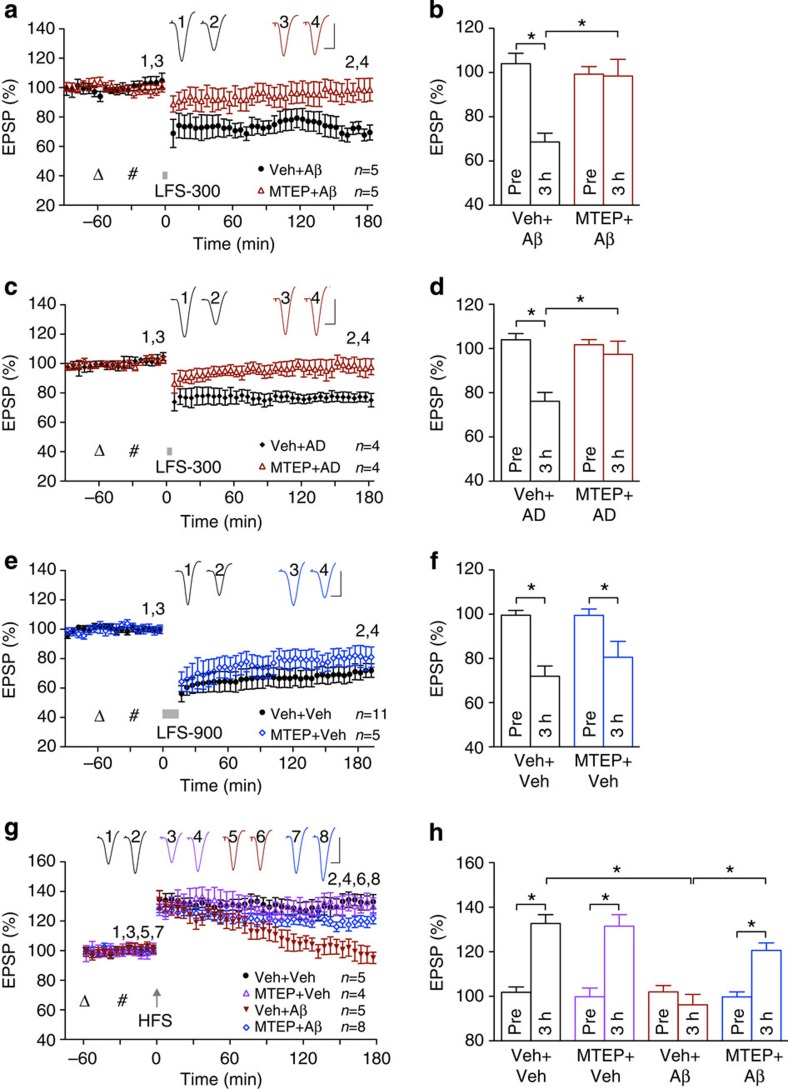
Figure 8. mGlu5R-dependence of Aβ-mediated disruption of both LTD and LTP but not control LTD or control LTP.
(a,b) Systemic administration of the selective mGlu5R antagonist MTEP (open triangle; 3 mg kg−1, i.p.) completely prevented the induction of LTD by LFS-300 (bar) in animals injected i.c.v. with soluble Aβ1–42 (hash) (68.6±4.0% in the vehicle+Aβ group, n=5, P<0.05 compared with Pre, and compared with 98.4±7.6% in the MTEP+Aβ group, n=5, P>0.05 compared with Pre; t-tests). (c,d) Similarly, MTEP completely prevented the induction of LTD in animals injected with Aβ-containing AD brain extract. As summarized in (d) the EPSP measured 76.2±3.6% in the vehicle+AD group, n=4, (P<0.05 compared with Pre, and compared with 97.4 ±5.6% in the MTEP+AD group, n=4, P>0.05 compared with Pre; t-tests). (e,f) In contrast, the same dose of MTEP that prevented Aβ-facilitated LTD failed to significantly affect control LTD induced by LFS-900 (72.0±4.4% in the vehicle+vehicle group, n=11, P<0.05 compared with Pre, and P>0.05 compared with 80.6±7.2% in the MTEP+vehicle group, n=5, P<0.05 compared with Pre; t-tests). (g,h) i.c.v. injection of soluble Aβ1–42 (hash), at the dose that facilitated LTD, blocked LTP completely at 3 h post HFS. Although systemic administration of MTEP (3 mg kg−1) did not affect HFS-induced control LTP, it prevented Aβ-mediated impairment of LTP. As summarized in (h), HFS induced significant (P<0.05 compared with Pre; paired t) LTP in the vehicle control group (132.7±4.0%, n=5), MTEP+vehicle group (131.5±5.2%, n=4) and MTEP+Aβ group (120.6±3.4%, n=8), but not in the vehicle+Aβ group (96.2±4.7%, n=5), which was significantly different from the other groups (one-way ANOVA-Tukey). Values are mean±s.e.m. Calibration: vertical, 2 mV; horizontal, 10 ms.