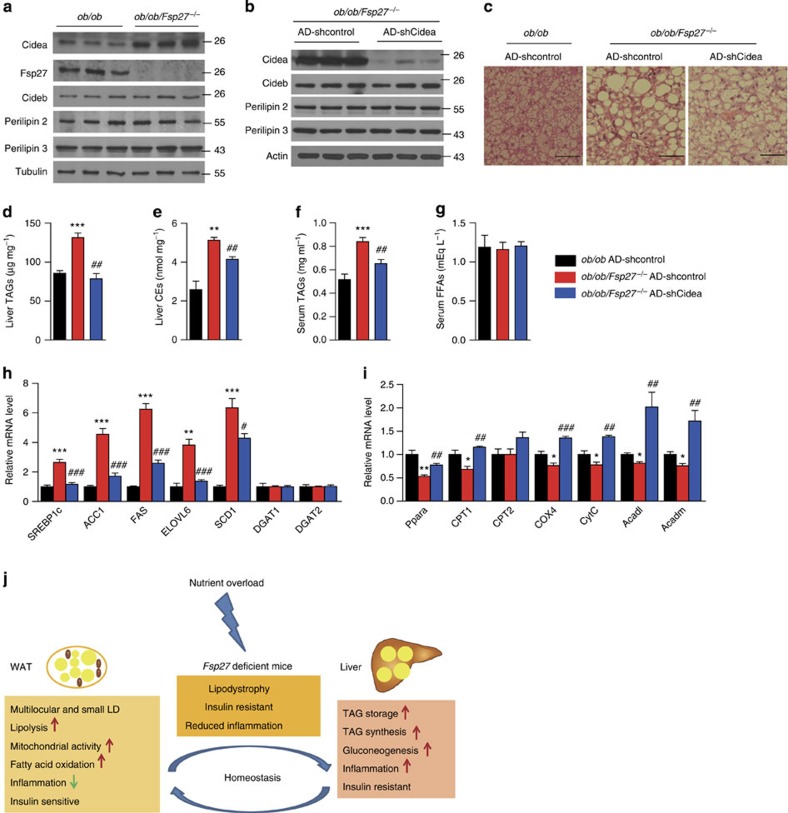
Figure 7. Liver-specific knockdown of Cidea alleviates hepatic stestosis in ob/ob/Fsp27−/− mice.
Four-month-old chow-fed ob/ob and ob/ob/Fsp27−/− mice were used to generate these data (a). Four-month-old chow-fed ob/ob or ob/ob/Fsp27−/− mice were injected with AD-shcontrol or AD-Cidea for 1 week before analysis (b–i). (a) Expression of the indicated proteins in the liver of ob/ob and ob/ob/Fsp27−/− mice. (b) Protein expression in the liver of ob/ob/Fsp27−/− mice injected with the indicated adenoviral vectors. (c) Liver H&E (haematoxylin and eosin) staining of ob/ob/Fsp27−/− mice injected with AD-shcontrol or AD-shCidea adenoviral vectors. Scale bar, 64 μm. (d) Liver TAG and (e) CE concentration in the livers of ob/ob and ob/ob/Fsp27−/− mice injected with the indicated adenovirusus (n=4). (f) Serum free fatty acid (n=7) and (g) TAG concentrations (n=6). (h,i) Relative mRNA expression levels in the livers of adenovirus injected ob/ob and ob/ob/Fsp27−/− mice (n=4 per group). (j) Proposed model for the role of Fsp27 in regulating metabolism. Quantitative data are presented as mean±s.e.m. Significance was established using a two-tailed Student’s t-test. Differences were considered significant at P<0.05.*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.