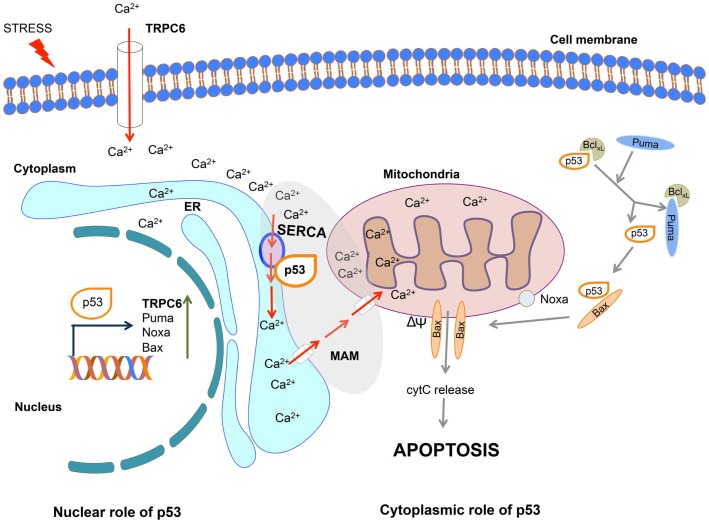
Figure 1.
Nuclear and cytoplasmic role of p53 in the induction of calcium-induced apoptosis. In response to stress, nuclear p53 activates the transcription of pro-apoptotic genes including TRPC6, Puma, Noxa, and Bax. Cytoplasmic p53 interacts with SERCA at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)/mitochondrial-associated membrane (MAM) junction, leading to the increase in Ca2+ influx, thereby promoting the loss of membrane potential (ΔΨ), release of cytochrome c, and induction of apoptosis. The entry of calcium into the cell is further enhanced through TRPC6 channel. Through this combined nuclear and cytoplasmic actions p53 promotes calcium-mediated apoptosis. For simplicity, the other apoptotic functions of p53 are not depicted in this diagram.