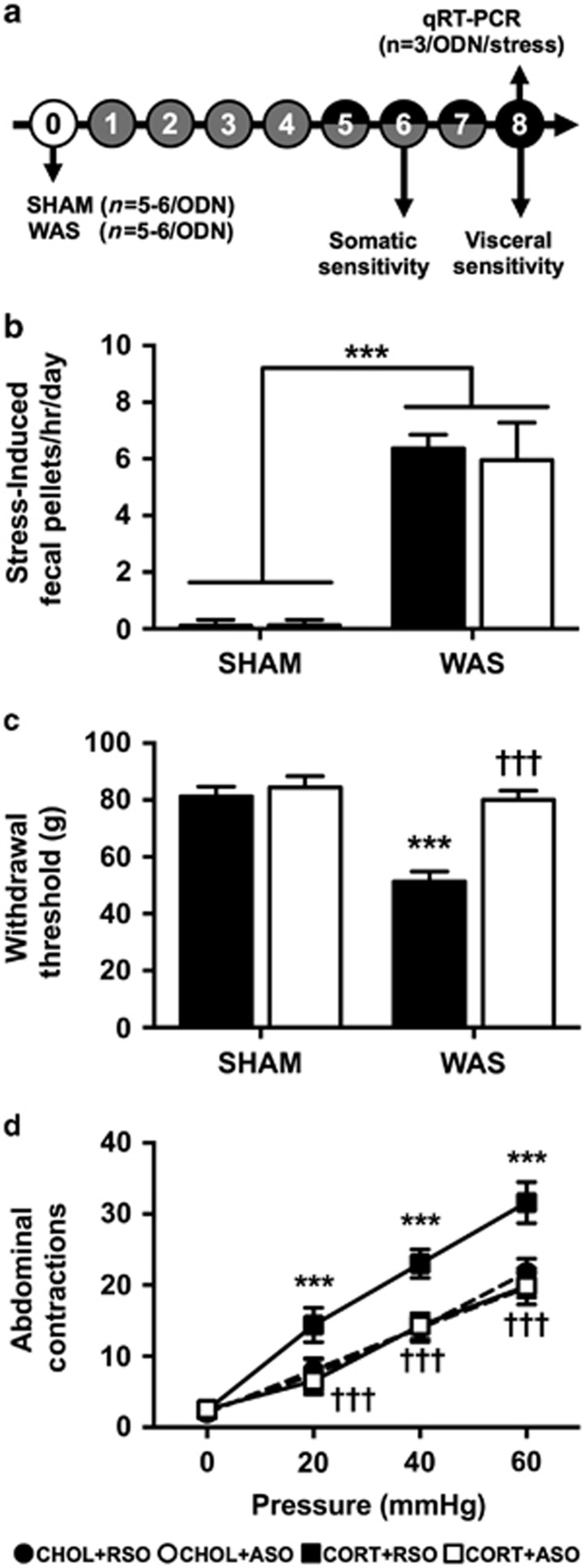
Figure 3.
Effect of ASO on WAS-induced behaviors. (a) Experimental design for repeated stress study. Experimental day is listed in each circle. Shaded circles indicate SHAM or WAS exposure. Filled circles represent ODN dosing. Both ODN dosing and stress exposure occurred on days 5–7. (b) WAS induced a significant increase in fecal pellet production on each day of exposure, which was not affected by ASO treatment. (c) WAS+RSO-treated rats demonstrated a significant decrease in withdrawal threshold that was not present in the WAS+ASO. (d) WAS+RSO induced a visceral hypersensitivity to colonic distension, which was normalized by ASO treatment. Data shown are mean±s.d. ***P<0.001 compared with SHAM+RSO, †††P<0.001 compared with WAS+RSO, two- or three-factor analysis of variance with or without repeated measures, Tukey–Kramer post hoc analysis. ASO, antisense oligodeoxynucleotide; ODN, oligodeoxynucleotide; RSO, random sense oligodeoxynucleotide; WAS, water avoidance stress.