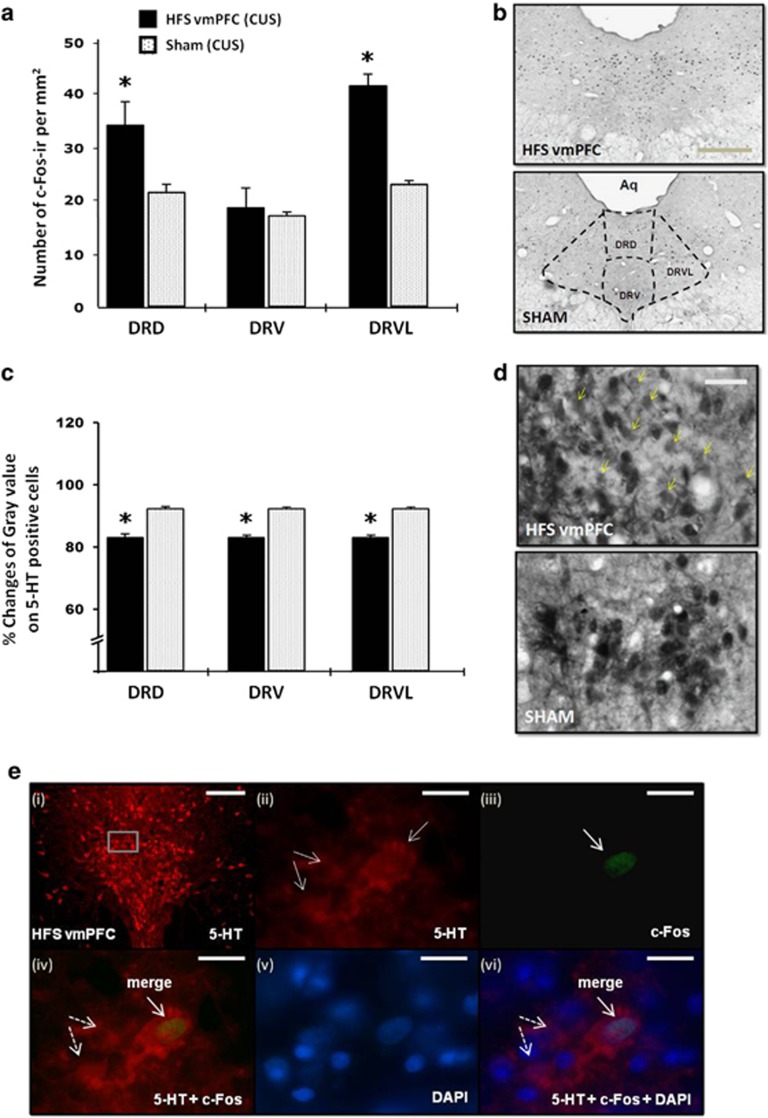
Figure 6.
Effects of vmPFC HFS on the c-Fos neural activity (a) and the percentage changes of mean gray value on 5-HT positive cells (c) in the DRN region of CUS animal model of depression. Representative photomicrographs of c-Fos (b; scale bar, 500 μm at × 4 magnification) and 5-HT (d; scale bar, 50 μm at × 40 magnification) histochemical staining of 30-μm-thick sections in the DRN. Note, vmPFC HFS resulted in higher levels of neuronal activation (that is, increased c-Fos positive cells) in the DRN areas as compared with the CUS sham animals. The small dots represent c-Fos-ir cells per mm2. Meanwhile, vmPFC HFS caused a remarkable reduction of optical density of 5-HT containing cells in the DRN area, indicating a local release of 5-HT, which increases in extracellular 5-HT in the DRN and forebrain projection areas. Representative high-power confocal images (e) are shown for the localization of 5-HT (red; e-i and -ii) and c-Fos (green; e-iii) immunofluorescence positive cells. DAPI (blue; e-v) was used as a nuclear stain. Merged images demonstrated the co-localization (arrows) of 5-HT and c-Fos (e-iv), as well as counterstained with DAPI (e-vi) in the DRD. Dotted arrows demonstrated non-c-Fos 5-HT positive cells (e-iv and -vi). Scale bar for fluorescent images: 100 μm (e-i) at low-power magnification; and 20 μm (e-ii–vi) at × 100 magnification. Significant difference from the CUS sham animals, *P<0.05. 5-HT, 5-hydroxytryptamine, serotonin; Aq, aqueduct; CUS, chronic unpredictable stress; DAPI, 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; DRN, dorsal raphe nucleus dorsal part; DRV, dorsal raphe nucleus ventral part; DRVL, dorsal raphe nucleus ventrolateral part; HFS, high-frequency stimulation; vmPFC, ventromedial prefrontal cortex.