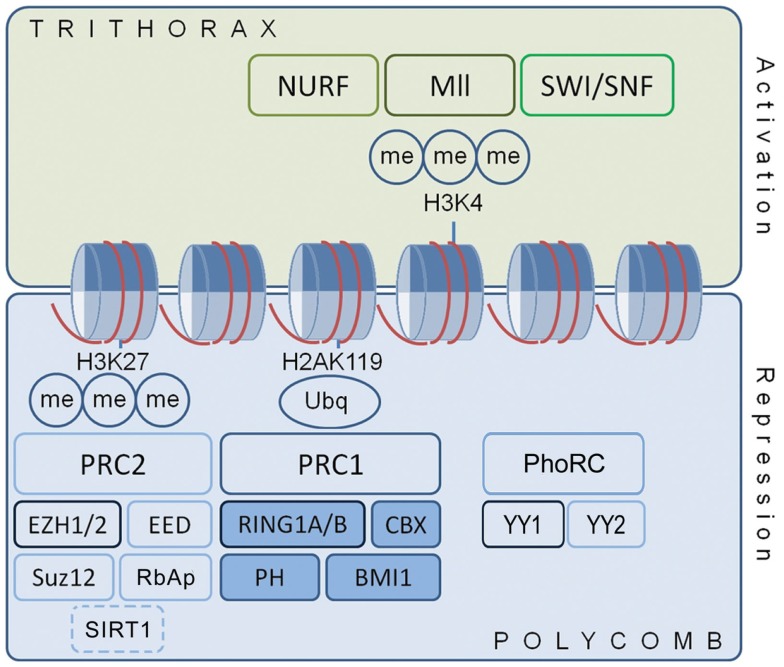
Figure 1.
Polycomb and trithorax proteins regulate chromatin structure and gene expression. Cartoon shows polycomb protein complex organization in relation to transcription. PcG proteins regulate chromatin structure through histone tail methylation and other post-translational modifications. PcG proteins often localize about discrete genetic elements with the functionally antagonist trithorax proteins, a diverse group of transcriptional activators, to yield a bivalent, “primed” state that is amenable to rapid alteration in response to signaling events. Ancillary DNA-binding proteins, such as YY1 of the Pho Repressive Complex, aid recruitment of PRC1 and PRC2 to target genes. They also interact with other DNA and chromatin modifiers, including DNMTs, histone deacetylases, histone acetyltransferases, and the Jarid pathway proteins. H2A and H3, histone 2A and histone 3; Me, methyl group; PRC, polycomb repressive complex; Ubq, ubiquitin.