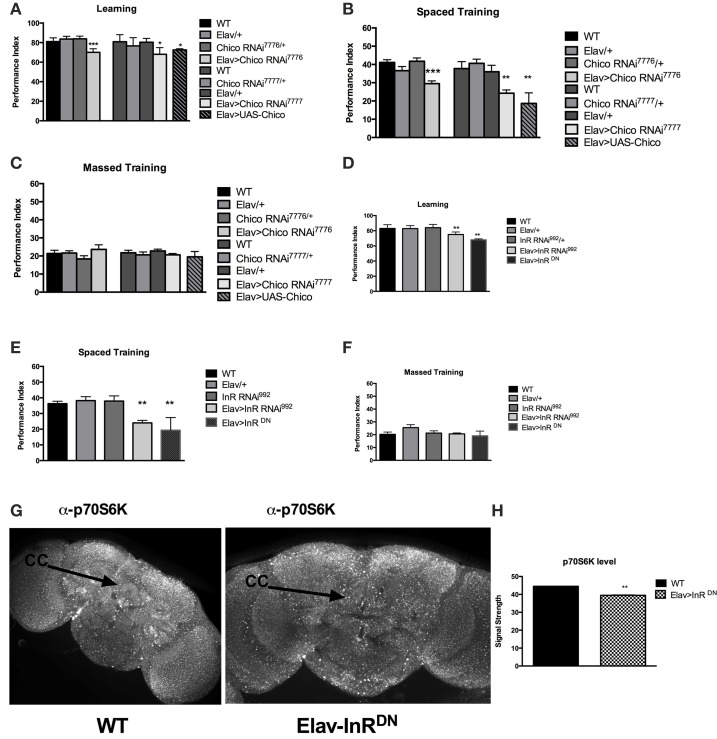
Figure 1.
Pan-neuronal disruption of Insulin signaling results in memory defects. (A) Learning is significantly defective in Drosophila expressing UAS-RNAi against the insulin receptor substrate, chico pan-neuronally. We expressed 2 different RNAi constructs: [Elav>ChicoRNAi7776] (P = 0.005, N = 6 PI per genotype) and [Elav>ChicoRNAi7777] (P = 0.0104, N = 6 PI per genotype). In addition, pan-neuronal overexpression of chico [Elav>UAS-chico] led to a significant (P = 0.0015, N = 8 PI per genotype) defect in learning. The genetic controls ElavGAL4 [Elav/+], chicoRNAi [chicoRNAi7776], [chicoRNAi7777] and InRRNAi [InRRNAi992] show no defects compared to wild-type flies [WT]. (B) 1-day memory after spaced training is impaired by loss or gain of function of chico in neurons. RNAi against chico resulted in significant defect in 1 day memory for both constructs [Elav>ChicoRNAi7776] (P < 0.00001, N = 8 PI per genotype); [Elav>ChicoRNAi7777] (P < 0.00001, N = 8 PI per genotype). Overexpression of chico [Elav>UAS-chico] also resulted in significant defect in 1 day memory (P = 0.0004, N = 8 PI per genotype) (C) No significant defects in 1 day memory after massed training were observed between Chico RNAi or UAS-chico expressing flies compared to genetic controls (N = 8 PI per genotype). (D) Similarly, pan-neuronal disruption of Insulin receptor leads to learning defects either via expression of UAS-InR RNAi [Elav>InR RNAi992] (P = 0.0082, N = 4 PI per genotype) or with the expression of a dominant negative InR [Elav>InRDN] (P < 0.00001, N = 4 PI per genotype). There was no significant defect in any of the genetic appropriate controls. (E) Significant defects in 1 day memory after spaced training were also observed in transgenic flies expressing [Elav>InR RNAi992] (P < 0.00001, N = 8 PI per genotype) or [Elav>InRDN] (P = 0.0052, N = 8 PI per genotype). (F) No significant defects were seen in flies expressing InR RNAi or DN or in the appropriate genetic controls. (G) Representative level of p70S6K in the brain of WT and flies expressing InRDN pan-neuronally [Elav>InRDN]. (H) Significant decreased level of p70S6K is observed in Elav>InRDN flies (N = 5 brains per genotype, P = 0.0022) All graphs depict mean ± s.e.m. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.001; ***p < 0.0001.