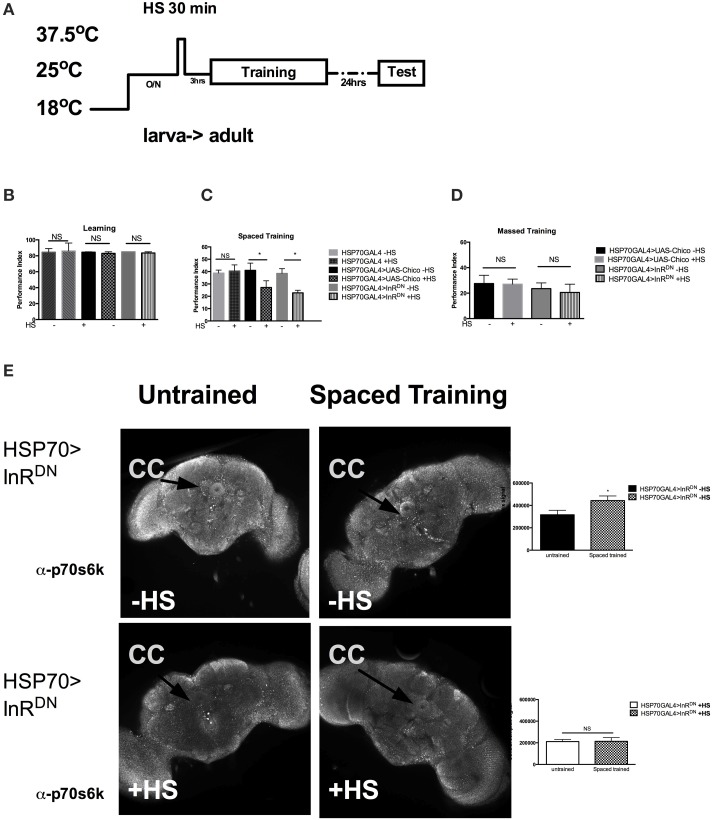
Figure 3.
Insulin signaling is acutely required for memory formation. (A) Protocol used to express the transgenes acutely in adult. The protocol depicted is for 1 day memory after spaced training. For learning, the testing immediately follows training. (B) Acute expression of UAS-chico [HSP70GAL4>UAS-chico +HS] (P = 0.5425) or InRDN [HSP70GAL4>InRDN +HS] (P = 0.4226, N = 2 PI per genotype) does not affect learning. (C) Acute expression of UAS-chico [HSP70GAL4>UAS-chico +HS] (P = 0.0316, N = 8 PI per genotype) or InRDN [HSP70GAL4>InRDN +HS] (P = 0.0069, N = 8 PI per genotype) disrupts memory after spaced training. (D) No defect is seen after the same treatment in 1 day memory after massed traininig (P > 0.05, N = 2 PI per groups). (E) The first row shows representative brains immunohistochemistry with p70s6k from HSP70GAL4>InRDN—HS flies with mock training (presented with odors but no shock) vs. spaced training. The second row shows representative brain immunohistochemistry with p70s6k from HSP70GAL4>InRDN +HS with mock vs. spaced training. Quantification of the signal strength in the central complex shows a significant (P = 0.0351, N = 4 biological replicates per group) increase after spaced training compared to mock training in HSP70>InRDN flies only when not exposed to heat shock. All graphs depict mean ± s.e.m. *p < 0.05.