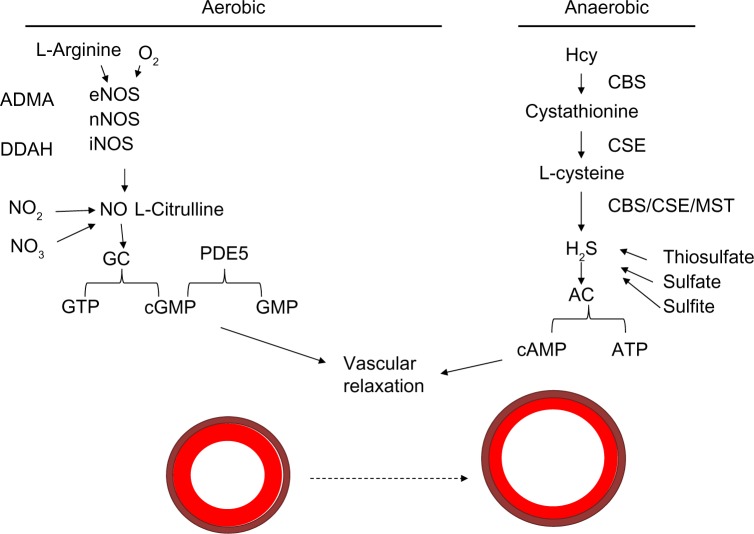
Figure 3.
Mechanism of vasodilation.
Notes: H2S can be acquired via various conversion steps of Hcy in an anaerobic pathway. Hcy is converted to cystathionine by CBS and then to L-cysteine by the CSE enzyme. L-Cysteine can be converted to H2S, which is used by adenylyl cyclase to convert ATP to cAMP involved in vasorelaxation. The substrates oxygen and L-arginine are known to be used by eNOS, nNOS, and iNOS enzymes to produce nitric oxide, which potentiates guanylyl cyclase to convert GTP to cGMP. cGMP is a molecule that allows for vascular relaxation. PDE5 inhibits vasorelaxation, as its activation converts cGMP to GMP and potentiates vasoconstriction.
Abbreviations: Hcy, homocysteine; CBS, cystathionine β-synthase; CSE, cystathionine γ-lyase; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthetase; nNOS, neuronal NOS; iNOS, inducible NOS; GTP, guanosine triphosphate; cGMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate; PDE, phosphodiesterase; ADMA, asymmetric dimethylarginine; DDAH, dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase; MST, 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase; GC, guanylyl cyclase; AC, adenylyl cyclase.