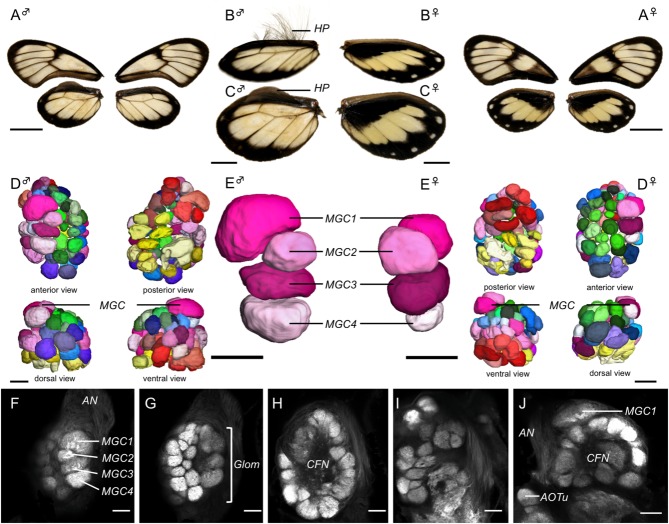
Figure 2.
Sexual dimorphism in the wings and antennal lobes (AL). A–C: Wing morphology in males (♂) and females (♀) showing wing pigmentation on the dorsal surface (A) and the presence of hair-pencils (HP) on the hind wings of males from an oblique anterodorsal view (B) and a direct dorsal view (C). D,E: Surface reconstructions of the full complement of AL glomeruli (D), and of the subset of four glomeruli that form the macroglomerular complex (MGC1–4 in E). Among the ordinary glomeruli, green tones indicate the dorsalmost glomeruli, blue tones the middle layer, pink tones the posterior layer, red tones the posterodorsal glomeruli and yellow tones the posteromedial glomeruli. F–J: Synapsin immunofluorescence in single confocal sections of the AL. F–I: Frontal sections that move progressively deeper into the AL until reaching its posterior boundary. The four distinct glomeruli of the MGC (MGC1–4 in F) occupy the most anterior position in the AL, close to the root of the antennal nerve (AN in F). The ordinary glomeruli (Glom in G) surround the central fibrous neuropil (CFN in H,J). J: A horizontal section at the level of the anterior optic tubercle (AOTu) and shows MGC1 protruding from the general spherical shape of the AL. Scale bars = 1.0 cm in A; 0.5 cm in B,C; 50 μm in D–J.