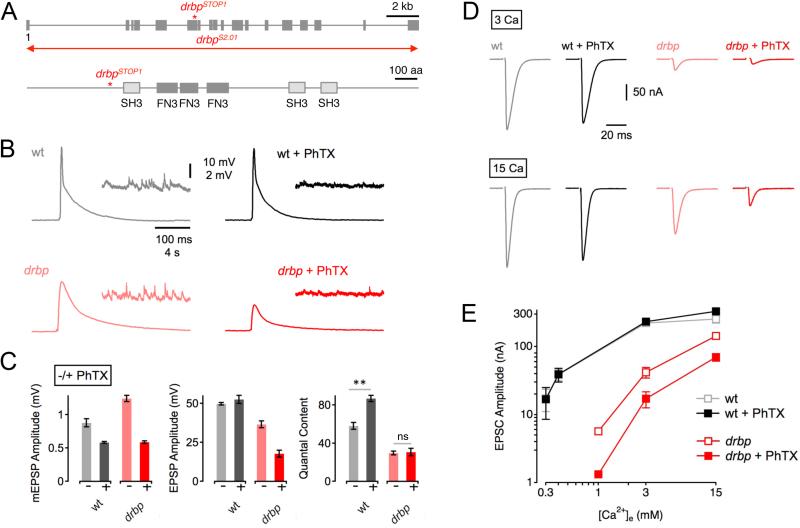
Figure 1. RIM-Binding Protein Is Required for Homeostatic Synaptic Plasticity.
(A) Top: Schematic of the drbp locus indicating the approximate location of the drbpSTOP1 mutation. The 19 coding exons are represented by gray boxes ('1' denotes the first exon), and the red line refers the approximate location of the drbpS2.01 deletion. Bottom: Schematic of RBP protein structure. Boxes denote the locations of the Src homology 3 domains (SH3), and the fibronectin type 3 (FN3) domains.
(B) Representative traces of EPSPs and mEPSPs for wild type in the absence and presence of PhTX (gray and black data; respectively), and drbpSTOP1 placed over the deficiency drbpS2.01 in the absence and presence of PhTX (‘drbp’; light red, and dark red data; respectively; 1.5mM [Ca2+]e).
(C) Average mEPSP amplitudes (left), EPSP amplitudes (middle), and quantal content (EPSP/mEPSP; right) of the indicated genotypes minus PhTX (light gray/red) and plus PhTX (black, dark red). w1118 (−PhTX): n=8; w1118 (+PhTX): n=7; drbp (−PhTX): n=16; drbp (+PhTX): n=17.
(D) Sample EPSCs of the indicated genotypes in the absence and presence of PhTX (‘−/+ PhTX’) at 3mM [Ca2+]e (top row) and 15mM [Ca2+]e (bottom row).
(E) Relationship between mean EPSC amplitude and extracellular Ca2+ concentration in wild type (control: light gray, n=4–7 per [Ca2+]e; PhTX: dark gray, n=4–7 per [Ca2+]e), and drbp (control: light red, n=8–12 per [Ca2+]e; PhTX: dark red, n=6–12 per [Ca2+]e). The wild-type data for the two lowest [Ca2+]e were already published (Müller et al., 2012).