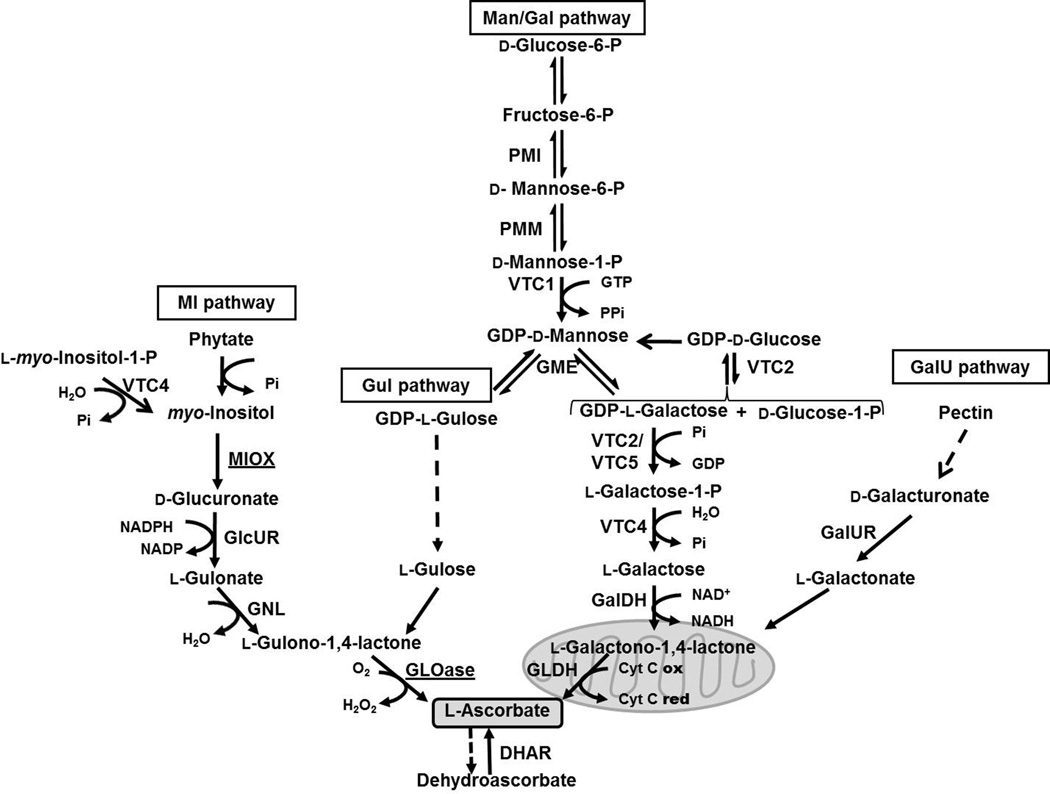
Figure 1.
Pathways involved in ascorbate biosynthesis and regeneration in plants: The d-mannose/l-galactose (Man/Gal) route, the l-gulose (Gul) shunt, the d-galacturonate (GalU) pathway, and the myo-inositol (MI) route. A purple acid phosphatase with phytase activity has been shown to channel phytate to the MI pathway, while VTC4 has been shown to also use l-myo-inositol-1 phosphate and contribute to both myo-inositol and ascorbate metabolisms. The enzymes participating in the Man/Gal route are: Phosphoglucose isomerase (EC 5.3.1.9); phosphomannose isomerase (PMI, EC 5.1.3.1.8); phosphomannose mutase (PMM, EC 5.4.2.8); GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase (VTC1, EC 2.7.7.13); GDP-mannose-3’,5’-epimerase (GME, EC 5.1.3.18); GDP-galactose phosphorylase (VTC2, EC 2.7.7.B2); l-galactose-1-phosphate phosphatase (VTC4); l-galactose dehydrogenase (GalDH, EC 1.1.1.48); l-galactono-1,4-lactone dehydrogenase (GLDH, EC 1.3.2.3). The enzymes in the GalU pathway are: d-galacturonate reductase (GalUR) and gluconolactonase (EC 3.1.1.17). The enzymes in the MI pathway are: Inositol phosphate phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.25); myo-inositol oxygenase (MIOX, EC 1.13.99.1); glucuronate reductase (GlcUR, EC 1.1.1.19); gluconolactonase (GNL, EC 3.1.1.17), and l-gulono-1,4-lactone oxidase (GLOase, EC 1.1.3.8). The enzymes involved in AsA recycling are: Monodehydroascorbate reductase (MDHAR, EC. 1.6.5.4), and dehydroascorbate reductase (DHAR, EC 1.8.5.1). Where omitted EC number have not been assigned. GLDH is a known mitochondrial enzyme. In this study we analyzed in detail Arabidopsis lines constitutively expressing MIOX and GLOase, enzymes in the MI pathway (underlined).