Figure 1. Different antibiotics induce distinct changes to C. difficile infection resistance and intestinal microbiota composition.
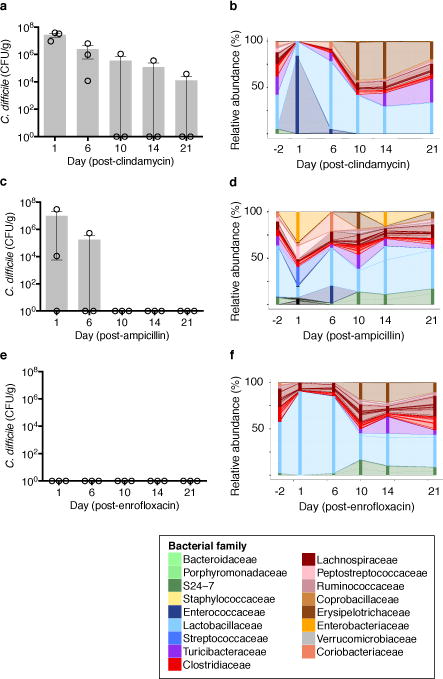
Susceptibility to C. difficile infection following clindamycin (a), ampicillin (b), or enrofloxacin (c). Correlation of C. difficile CFU and toxin in cecal content following infection (d). Intestinal microbiota composition at timepoints indicated (e,f,g). Each stacked bar represents the mean microbiota composition of three separately-housed animals. ****P<0.0001. Center values (mean), error bars (s.e.m.) (a, b, c).
