Figure 5.
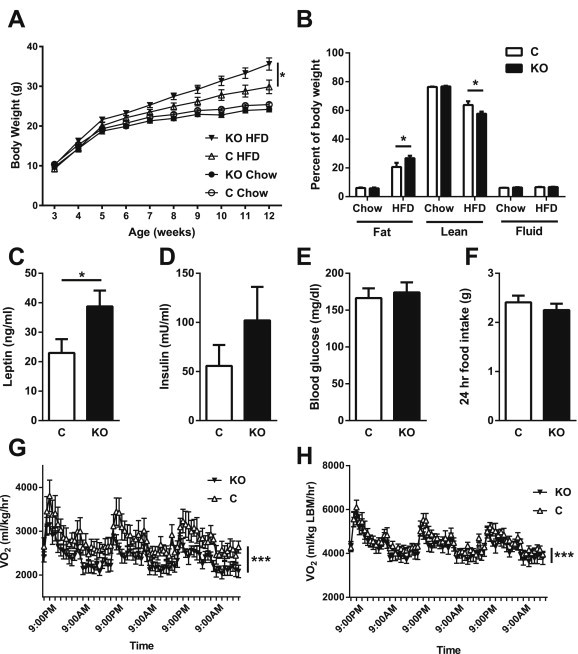
Leptin regulation of Pdyn neurons is required for normal energy homeostasis in DIO mice. Male LepRbPdynKO (KO) and littermate controls (C) were placed on chow or high fat diets, and body weight measured weekly (A) (mean ± SEM is shown; *p < 0.05 by ANOVA). At 12–14 weeks of age, animals underwent body composition analysis by NMR spectroscopy (B). Serum from HFD-fed control and LepRbPdynKO mice was assayed for leptin (C) or insulin (D). Blood glucose was measured following a 24 h fast (E) in the HFD cohort. (B–E) mean ± SEM is shown; *p < 0.05 by t-test. (F–H) A subset of HFD-fed control and LepRbPdynKO mice were assessed in CLAMS metabolic cages for 3 days following body composition analysis. Food intake (F) was measured on the final day. VO2 was also measured and is presented normalized to total body mass (G) and lean body mass (H) (Mean ± SEM is shown; ***p < .0001 by ANOVA). HFD, high fat diet (Research diets, 60% kcal from fat). Black triangles = HFD fed LepRbPdynKO; white triangles = HFD fed controls; black circles = chow fed LepRbPdynKO; white circles = chow fed controls. Black bars = LepRbPdynKO; white bars = controls. N = 8–14 for chow and HFD cohorts. N = 6–7 animals per genotype for VO2 measurements.
