Figure 2.
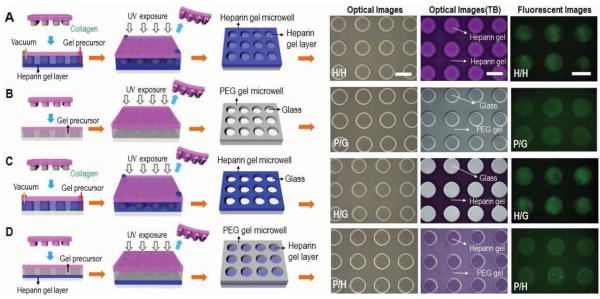
Schematic illustration of four variants of hydrogel microstructures tested in our study. A) Heparin microwells on the heparin gel-coated glass surface (H/H). B) PEG microwells on the glass surface (P/G). C) Heparin gel microwells on the glass surface (H/G). D) PEG microwells on the heparin gel-coated glass surface (P/H). Optical and fluorescent microscopic images of the four kinds of gel microstructures before and after toluidine blue (TB) staining as well as after collagen coating. Scale bar = 200 μm. B) and D) PEG hydrogel microwells were simply fabricated by micromolding technique and then collagen was selectively absorbed on bottom of microwells by immersing in collagen solution due to anti-fouling effect of PEG microwell. A,C) Heparin hydrogel microwells were fabricated by a combination of micromolding and microcontact printing. Collagen transfer by microcontact printing was concurrent to micromolding procedure.
