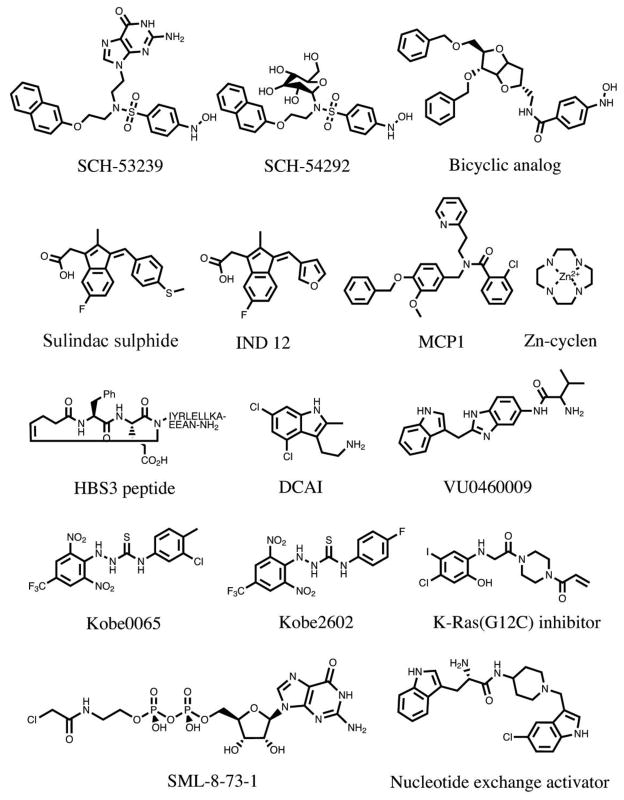
Figure 2. Compounds that have been reported to bind to Ras.
SCH-53239 was designed to inhibit guanine nucleotide exchange27. Structure-activity relationship studies led to the development of a derivative with greater water solubility, SCH-54292. Subsequently, another group used molecular modeling to design a series of sugar-derived bicyclic analogs28. Based on earlier observations that the NSAID sulindac showed anti-tumour activity in Hras-mutant rat mammary carcinomas224, the active metabolite sulindac sulphide was evaluated and found to bind to H-Ras29. IND12 is a sulindac derivative that blocks the growth of Ras-transformed cells31,32. MCP1 was identified in a yeast two-hybrid screen for inhibitors of H-Ras binding to full length Raf-134. Zn-cyclen selectively binds and stabilizes the weak effector binding affinity conformational state of Ras35. The HBS3 peptide is a mimic of the Sos1 αH helix that interacts with H-Ras36. DCAI and VU0460081 were identified in fragment-based library screens for K-Ras4B-binding molecules35,36. Kobe0065 was identified in a computer docking screen of a virtual compound library and selected for its ability to inhibit H-Ras-GTP binding to Raf-RBD40. Kobe2602 was identified in a subsequent computer-assisted similarity search of 160,000 compounds. A K-Ras G12C inhibitor was identified using a disulphide-fragment-based screening approach with GDP-bound K-Ras G12C. SML-8-73-1 covalently binds to K-Ras G12C and occupies the nucleotide binding site44. The Nucleotide exchange activator (compound 4) stimulates Ras-GTP formation, yet disrupts ERK and PI3K signalling45.