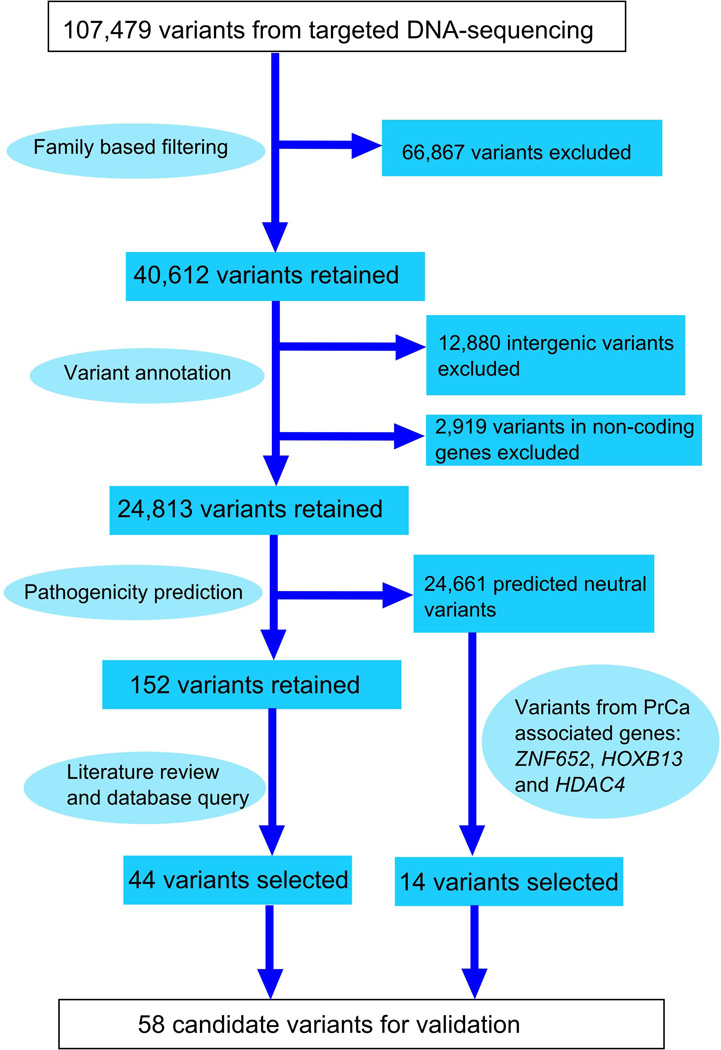
Figure 1. A flowchart describing the variant characterization pipeline.
The targeted re-sequencing of 2q37 and 17q11.2-q22 from 68 Finnish HPC family members produced a total of 107,479 unique sequence variants. Family-based filtering excluded 66,867 variants that did not co-segregate with affection status. Annotation enabled the selection of 24,813 variants that were located within protein-coding genes. Pathogenicity predictions were performed in silico using MutationTaster, PolyPhen-2 and PON-P. As a result, the number of candidate variants was reduced to 152. The final filtering step exploited diverse information on genes and variants as well as gene ontology and pathway data stored in several public databases. In addition, select HDAC4, ZNF652 and HOXB13 variants, which were predicted to be non-pathogenic, were included in the validation because these genes have been associated with PrCa in previous studies.