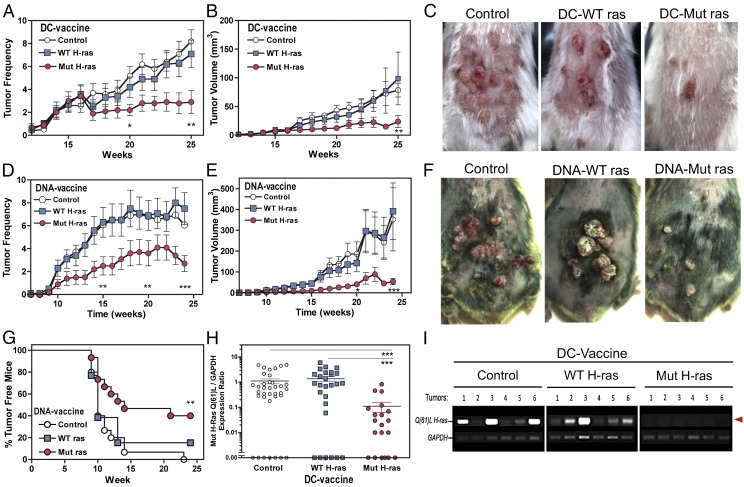
FIGURE 4.
Immunoprevention against chemical carcinogenesis in two mouse strains and evidence for immunoediting. (A–C) Engineered DC-based vaccination of A/J mice. Mice were immunized twice with the indicated DC vaccine, then subjected to DMBA/TPA carcinogenesis over 25 wk (n = 20 per group). The individual number of tumors per mouse (A) and the average tumor volume per mouse (B) per group are shown (mean ± SEM). Tumor incidence and growth rates were inhibited by 70% and 90%, respectively (the Tukey significance test, p < 0.01). (A and B) Two-way ANOVA and the Tukey posttest calculated significance are indicated: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. (C) Photodocumentation of representative mice per vaccination group is shown. (D–G) DNA-based epicutaneous vaccination of C3H/HeN mice. Mice received three vaccinations over 15 d, then were subjected to DMBA/TPA carcinogenesis over 24 wk (n = 20 per group). (D) The average tumor numbers per mouse in each group. (E) The average tumor volume per mouse in each group. The Mut H-ras DNA–vaccinated group developed 50% fewer tumors, and tumor growth was inhibited by >85% (p < 0.01, p < 0.001, respectively). (F) Representative photographs of tumors that develop in DNA-vaccinated mice. (G) Tumor-free plot. Tumor penetrance was inhibited in C3H/HeN mice immunized with Mut H-ras DNA–based vaccine. Tumor-free mice are defined as having no tumors or only small tumors < 3 mm3. (H and I) Immunoediting in tumors from Mut H-ras–vaccinated mice. (H) Relative quantification of Mut H-ras mRNA expression levels in individual tumors. The densitometry ratio for Mut H-ras ACB-PCR and matched GAPDH amplicon products of each tumor sample, as shown for six tumors in (I), as individual data points. The number of tumors screened was as follows: PBS, n = 30; DC–WT H-ras, n = 25; DC–Mut H-ras, n = 20. Expression was negligible in 45% of tumors from Mut H-ras–vaccinated mice and in 15–22% of tumors from the control groups. (G and H) Two-way ANOVA statistical significance is indicated: **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. (I) Loss of H-ras Q61L mutation expression in tumors from DC–Mut H-ras–vaccinated mice. The Q61L H-ras allele (upper band, red arrow) detected by ACB-PCR in mRNA from individual tumors harvested from A/J mice after 25 wk of carcinogenesis. GAPDH serves as an internal gene expression control.