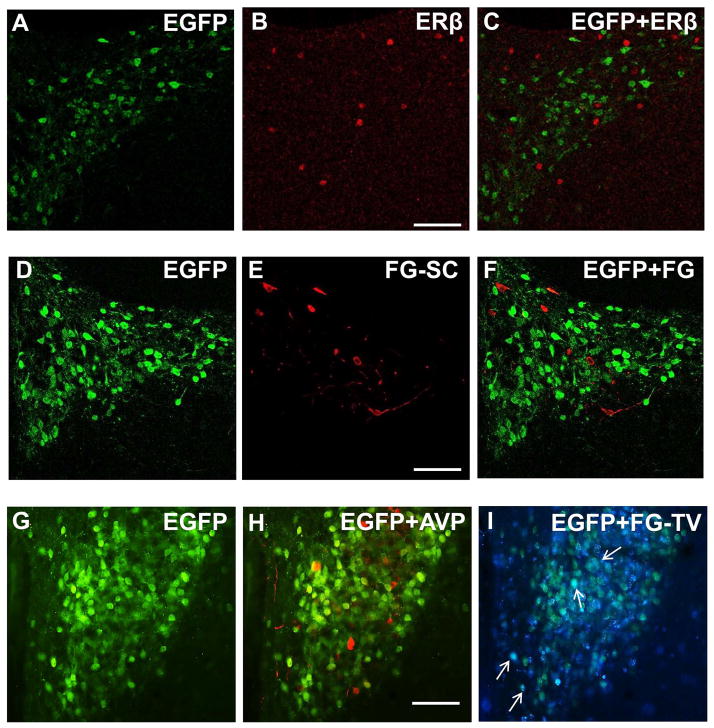
Figure 2. Distribution of AT1aR-EGFP-labeled cells in the PVN.
A–C: AT1aR-EGFP and estrogen receptor β (ERβ) labeling of PVN neurons; A: AT1aR-EGFP PVN neurons (green) labeled with anti-GFP antiserum; B: PVN neurons labeled with anti-ERβ antiserum (red); C: merge of A and B showed no co-localization of GFP and ERβ. D–F: Spinally projecting PVN neurons; D: AT1aR-EGFP PVN neurons (green) labeled with anti-GFP antibody; E: PVN neurons labeled with fluorogold (FG, red) after injection into the spinal cord (FG-SC); F: Merge of D and E showed no co-localization of GFP and FG. G–I: AT1aR-EGFP, arginine-vasopressin (AVP) and tail vein-injected FG labeling of PVN neurons; G–I: PVN section triple labeled for GFP, AVP and FG following tail-vein (FG-TV) injection. G. AT1aR-EGFP PVN neurons (green) labeled with anti-GFP antiserum; H: No co-localization of GFP (green) and AVP (red) was observed; I: Scarce co-localization (white arrows) of GFP (green) and FG-TV (blue) was observed. Scale bars A–I = 0.5 mm.