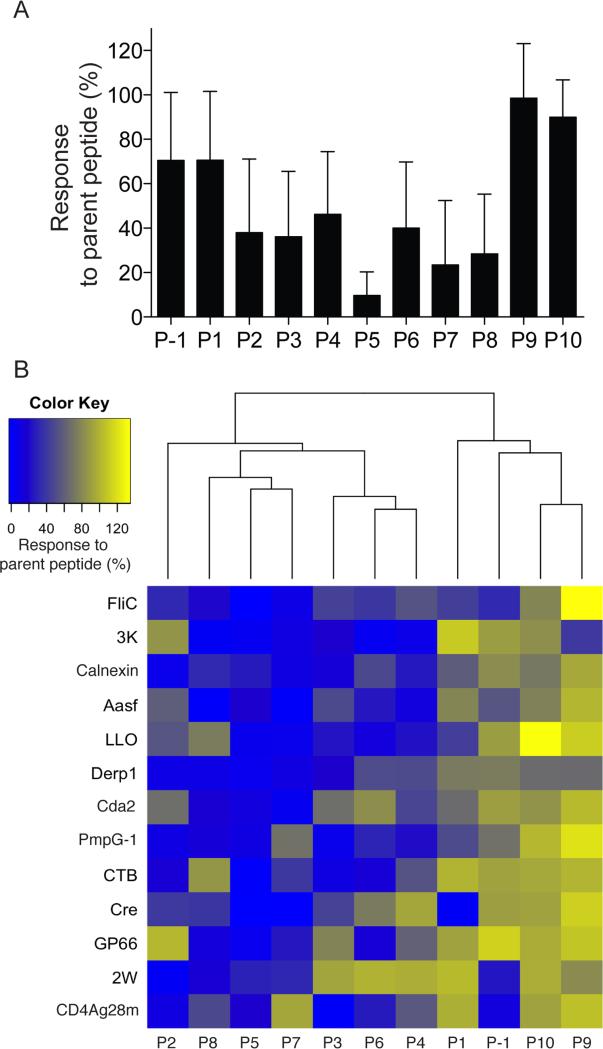
Figure 2. Alanine substitution analysis of CD4+ T cell responses to known foreign epitopes.
(A) Eleven amino acid versions of the indicated peptides (nonamer cores shown Table 1 plus P-1 and P10, nonamer core WFPAEPEDV for Cre) with single alanine substitutions at the indicated positions were tested as stimulators of parent peptide-primed CD4+ T cells in an ELISPOT assay. The % of the response to the parent peptide was determined by dividing the number of spots stimulated by the alanine substituted peptide by the number of spots stimulated by the parent peptide and multiplying by 100. The bars represent the average (± SD, n = 3 mice) values for the parent peptides shown in (B) from 2 independent experiments. (B) Unsupervised clustering of the % of response to the parent peptide after stimulation with alanine-substituted peptides for each of the 13 indicated parent peptides.