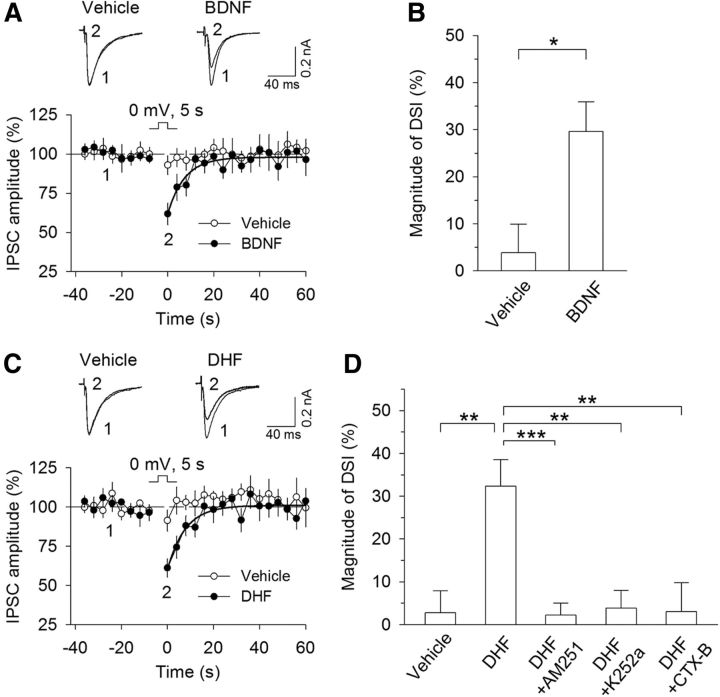
Figure 1.
TrkB receptor agonists enabled DSI in VTA dopamine neurons. A, A brief depolarization (5 s from −70 to 0 mV) did not induce significant depression of IPSCs in VTA dopamine neurons, whereas bath application of BDNF (20 ng/ml) enabled DSI. Shown are sample traces of evoked IPSCs (top) and averaged DSI (bottom). Solid lines indicate single exponential fitting curves of the decay of DSI. B, Summary of the magnitude of DSI in the presence of vehicle or BDNF (20 ng/ml) (n = 8 or 9). *p < 0.05. C, D, Bath application of TrkB receptor agonist DHF (10 μm) enabled DSI (n = 10 or 11; **p < 0.01), which was blocked by the CB1 receptor antagonist AM251 (2 μm; n = 9; ***p < 0.001), the TrkB receptor inhibitor K252a (200 nm; n = 9; **p < 0.01), or the TrkB receptor antagonist CTX-B (100 nm; n = 12; **p < 0.01). Error bars indicate SEM.