Figure 6.
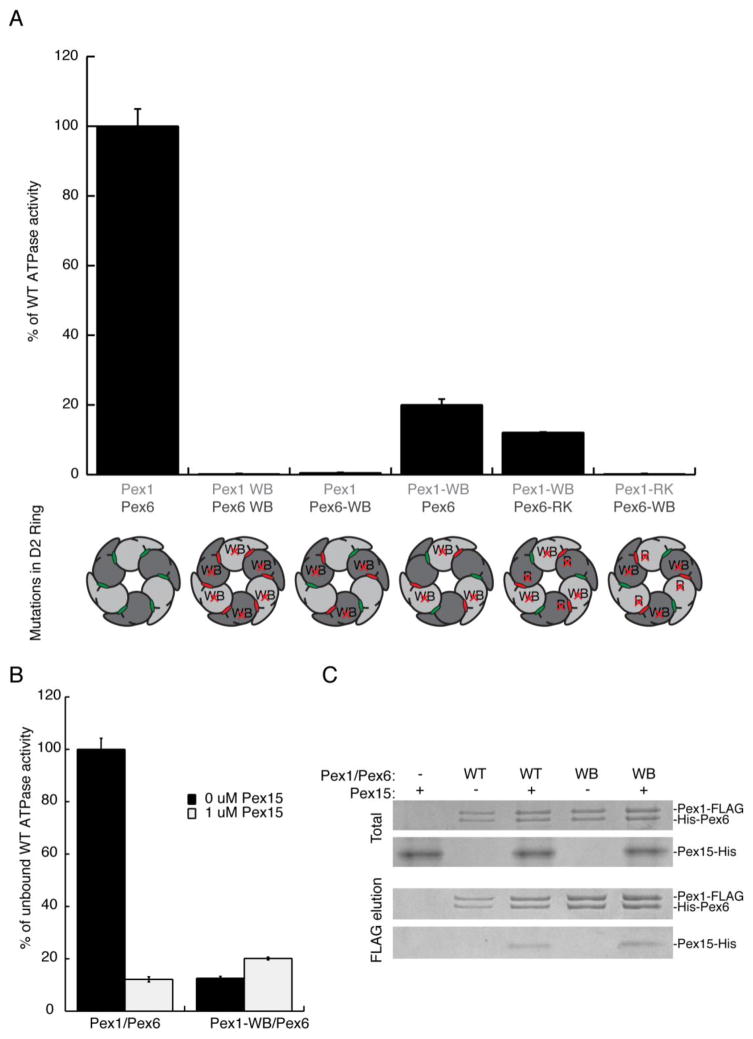
A) A comparison of ATPase activities for wild-type Pex1-FLAG/His-Pex6 and its variants with mutations in the D2 domains. The schematic below the graph indicates the D2 mutations made in the context of the heterohexamer, with Pex1 represented in light gray and Pex6 in dark gray. The ATP-binding sites are colored green when wild type and red when mutated. WB: Mutation of Glu to Asn in the Walker B motif, leading to inhibition of ATP hydrolysis. RK: Mutation of Arg to Lys in the R-finger, a residue contributed to the neighboring ATP-binding site, which inhibits ATP hydrolysis when mutated.
B) The cytoplasmic domain of Pex15 inhibits the ATPase activity of the wild-type Pex1/Pex6 complex, but not the Pex1-WB/Pex6 mutant.
C) The cytoplasmic domain of Pex15 co-immunoprecipitates with both wild-type and the D2 Walker B mutant Pex1/Pex6 complex. The immunoprecipitation was performed on purified proteins using the FLAG tag on Pex1.