Figure 2.
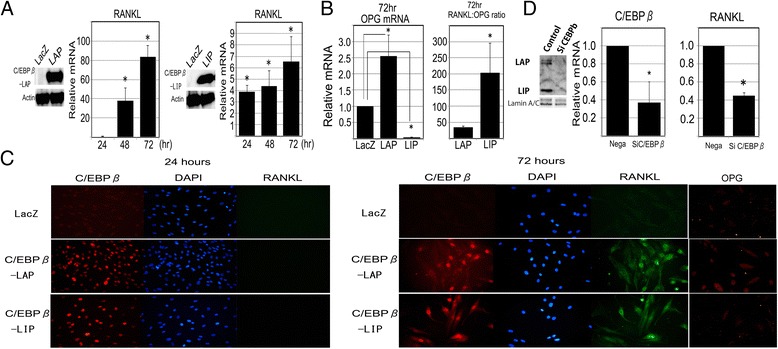
Gain and loss of function for C/EBPβ in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from the synovium of rheumatoid arthritis patients (RA-FLS). (A, B) Effect of C/EBPβ overexpression on RANKL and OPG expression in RA-FLS. RA-FLS were transfected with adenovirus expression vector for C/EBPβ-LAP, −LIP or LacZ (negative control) and cultured for 24 hours. Whole cell extracts were assayed by western blotting for C/EBPβ. RANKL and OPG mRNA expression were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR from three samples. The RANKL-OPG mRNA ratio with the over-expression of C/EBPβ-LAP or -LIP was calculated: *P <0.05 versus control using the Mann-Whitney U-test. (C) Immunofluorescence staining for RANKL or C/EBPβ protein in RA-FLS with overexpression of C/EBPβ-LAP, −LIP or LacZ control at 24 hours and 72 hours. Immunofluorescense staining for OPG was also performed in a different series of experiments with the same method at 72 hours. Original magnification, 400×. (D) Effect of C/EBPβ knockdown on RANKL mRNA expression in RA-FLS. RA-FLS transfected with siRNAs were cultured with 10 ng/ml IL-1β for 48 hours and the expression of C/EBPβ and RANKL mRNA were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR. The C/EBPβ expression was effectively reduced by siRNA C/EBPβ transfection as confirmed by western blotting for nuclear extracts. RANKL expression was significantly decreased to less than 50%: *P <0.05 versus control using the Mann-Whitney U-test.
