Figure 4.
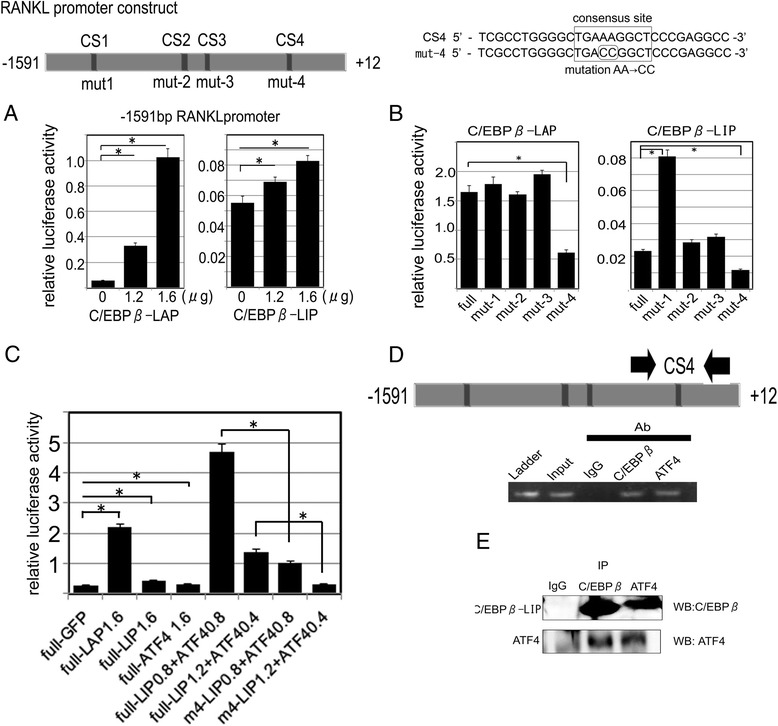
Transactivation of the human RANKL promoter by C/EBPβ and ATF4. Schematic of the constructs of the 1603 bp (−1591 bp ~ +12 bp) RANKL promoter, which were subcloned into the pGL-4.10 (luc2) vector. Analysis of the sequence indicated the presence of four C/EBPβ binding motifs (CS1-4). (A) The RANKL promoter-luciferase reporter vectors were co-transfected into HeLa cells with pCMV-LAP or pCI-LIP. Relative luciferase activity was assayed 24 hours post-transfection. (B) A 2-bp mutation (AA to CC) was made at one site (mut-1, mut-2, mut-3, mut-4). The RANKL promoter mutation constructs were co-transfected with pCMV-LAP or pCI-LIP into HeLa cells. (C) Cooperative effect of C/EBPβ and ATF4 on the RANKL promoter. Constructs of the RANKL promoter were co-transfected with expression vectors for C/EBPβ-LAP, −LIP, ATF4 or GFP. Synergistic activation of the promoter was observed with the combination of C/EBP-LIP and ATF4. The effect was diminished when the promoter harbored a mutation at CS4. Full: 1.6 kb human RANKL promoter; m4: 1.6 kb human RANKL promoter that has a mutation at CS4. (D) A chromatin immunoprecipitation assay was performed using C/EBPβ or ATF4 specific antibodies or control IgG in RA-FLS after treatment with IL-1β for 48 hours. The area containing the C/EBPβ consensus binding site 4 (CS4) on the RANKL promoter was amplified by semiquantitative RT-PCR. (E) Immunoprecipitation was performed using C/EBPβ or ATF4 specific antibodies or control in RA-FLS over-expressing C/EBPβ-LIP. Western blots for C/EBPβ or ATF4 showed a positive band for either C/EBPβ-LIP or ATF4.
