Figure 6. Additive effects of Dll1 and Dll4 blockade prevent heart rejection in CD8-depleted mice.
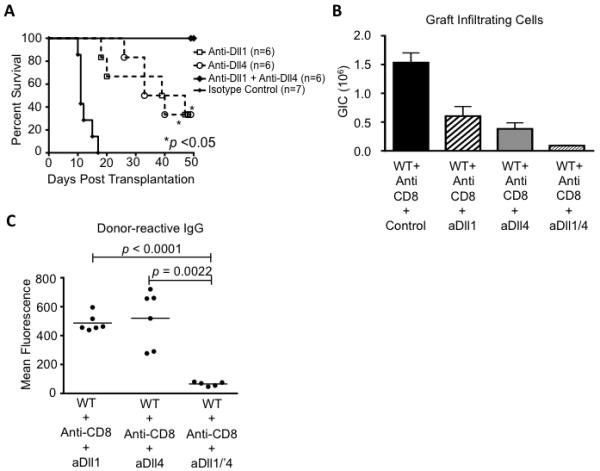
(A) After CD8 depletion, BALB/c heart allografts were established in B6 recipients treated with isotype control (anti-GD, n=7), anti-Dll1 (n=6), anti-Dll4 (n=6) or anti-Dll1+anti-Dll4 antibodies (n=6) (i.p. day 0, 3, 7, 10). Allograft survival was prolonged upon either Dll1 or Dll4 blockade alone (p<0.05). Upon combined Dll1/4 inhibition, no rejection was observed over the entire observation period (50 days); (B) Dll1, Dll4 and Dll1/4 blockade all decrease the number of graft-infiltrating cells at day of rejection or at termination of the experiment, but with more profound effects for combined blockade (p=0.028 vs. anti-Dll1 alone; p=0.038 vs. anti-Dll4 alone) (n=6-7/group); (C) Dll1/4 blockade but not isolated Dll1 or Dll4 inhibition prevents the accumulation of donor-reactive serum IgG antibodies (day 50 after transplantation).
